| | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
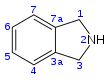
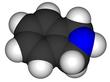
| IUPAC name 2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.955 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | C8H9N | ||
| Molar mass | 119.167 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Isoindoline is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C8H9N.[2] The parent compound has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is similar to indoline except that the nitrogen atom is in the 2 position instead of the 1 position of the five-membered ring. Isoindoline itself is not commonly encountered, but several derivatives are found in nature and some synthetic derivatives are commercially valuable drugs, e.g. pazinaclone.[3]
Substituted isoindolines
1-Substituted isoindolines and isoindolinones are chiral. Isoindolylcarboxylic acid and 1,3-disubstituted isoindolines are constituents of some pharmaceuticals and natural products. Isoindolines can be prepared by 1,2-addition of a nucleophile onto a bifunctional ε-benzoiminoenoates followed by intramolecular aza-Michael reaction. Another route involves [3+2] cycloaddition of the azomethine ylides (e.g. (CH2)2NR) to quinone in the presence of suitable catalysts. These methods have also been adapted to give chiral derivatives.[4][5][6]
Related compounds
- 4,7-Dihydroisoindole
- indole
- indene
- indoline
- benzofuran
- carbazole
- carboline
- isatin
- methylindole
- oxindole
- pyrrole
- skatole
- benzene
References
- ^ Isoindoline
- ^ Isoindoline
- ^ Speck Klaus; Magauer Thomas "The chemistry of isoindole natural products" Beilstein journal of organic chemistry 2013, vol. 9, pp. 2048-78. doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.243
- ^ Pandey, G.; Varkhedkar, R.; Tiwari, D (2015) Efficient Access to Enantiopure 1,3-disubstituted Isoindolines from Selective Catalytic Fragmentation of Original Desymmetrized Rigid Overbred Template, Org. Biomol. Chem., DOI: 10.1039/C5OB00229J
- ^ A Facile Access to Enantioenriched Isoindolines via One-Pot Sequential Cu(I)-Catalyzed Asymmetric 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition/Aromatization DOI: 10.1021/ol302987h
- ^ Asymmetric organocatalytic formal double-arylation of azomethines for the synthesis of highly enantiomerically enriched isoindolines DOI: 10.1039/B917246G