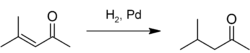 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one | |
| Other names Mesityl oxide Isobutenyl methyl ketone Methyl isobutenyl ketone Isopropylidene acetone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.002 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1229 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C6H10O |
| Molar mass | 98.145 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Oily, colorless to light-yellow liquid[1] |
| Odor | peppermint- or honey-like[1] |
| Density | 0.858 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −53 °C (−63 °F; 220 K) |
| Boiling point | 129.5 °C (265.1 °F; 402.6 K) |
| 3% (20°C)[1] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in most organic solvents |
| Vapor pressure | 9 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
Refractive index (nD) | 1.442 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements | H226, H302, H312, H332 |
GHS precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P501 |
| Flash point | 31 °C; 87 °F; 304 K [1] |
| Explosive limits | 1.4–7.2%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | 1120 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1000 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 710 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[2] |
LC50 (median concentration) | 1000 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr) 9000 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr) 10,000 mg/m3 (mouse, 2 hr) 2000 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 7 hr)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) | TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended) | TWA 10 ppm (40 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) | 1400 ppm[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | diacetone alcohol acetone, benzylideneacetone |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
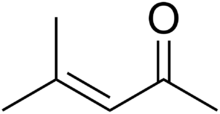
Mesityl oxide is a α,β-unsaturated ketone with the formula CH3C(O)CH=C(CH3)2. This compound is a colorless, volatile liquid with a honey-like odor.[3]
Synthesis
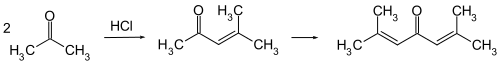
It is prepared by the aldol condensation of acetone to give diacetone alcohol, which readily dehydrates to give this compound.[4][5]
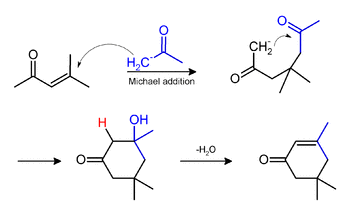
Phorone and isophorone may be formed under the same conditions. Isophorone originates via a Michael addition:
Phorone is formed by continued aldol condensation:
Uses
Mesityl oxide is used as a solvent and in the production of methyl isobutyl ketone by hydrogenation:[5]
Complete hydrogenation gives 4-methyl-2-pentanol (methyl isobutyl carbinol).
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0385". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "Mesityl oxide". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Merck Index, 14th Edition
- ^ Conant, J. B.; Tuttle, N. (1921). "Mesityl Oxide". Organic Syntheses. 1: 53. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.001.0053.
- ^ a b Sifniades, Stylianos; Levy, Alan B. (2000). "Acetone". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_079. ISBN 3527306730.