Dinitrobenzenes are chemical compounds composed of a benzene ring and two nitro group (-NO2) substituents. The three possible arrangements of the nitro groups afford three isomers, 1,2-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene. Each isomer has the chemical formula C6H4N2O4 and a molar mass of about 168.11 g/mol. 1,3-Dinitrobenzene is the most common isomer and it is used in the manufacture of explosives.
Properties
The dinitrobenzenes are all crystalline solids. The boiling points of the three isomers are relatively close; however, the melting points significantly differ. 1,4-Dinitrobenzene, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point.
| Dinitrobenzenes | |||
| IUPAC name | 1,2-Dinitrobenzene | 1,3-Dinitrobenzene | 1,4-Dinitrobenzene |
| Other names | o-Dinitrobenzene | m-Dinitrobenzene | p-Dinitrobenzene |
| Chemical structure | 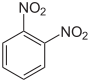 | 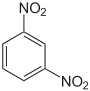 | |
| CAS number | 528-29-0 | 99-65-0 | 100-25-4 |
| 25154-54-5 (Unspecified isomers)[1] | |||
| PubChem | CID 10707 from PubChem | CID 7452 from PubChem | CID 7492 from PubChem |
| Chemical formula | C6H4N2O4 | ||
| Molar mass | 168.11 g/mol | ||
| Magnetic Susceptibility | -65.98·10−6 cm3/mol | -70.53·10−6 cm3/mol | -68.30·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Physical state | solid | ||
| Appearance | white solid | yellowish solid | pale yellow solid[2] |
| Melting point | 118 °C[3] | 89.6 °C[4] | 174 °C[5] |
| Boiling point | 318 °C[3] | 297 °C[4] | 299 °C[6] |
| Density | 1.565 g/cm3 (17 °C)[6] | 1.575 g/cm3 (18 °C)[6] | 1.625 g/cm3 (18 °C)[6] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.08 Pa (30 °C)[7] | 0.07 Pa (30 °C)[7] | |
| 0.34 Pa (50 °C)[7] | 0.23 Pa (50 °C)[7] | ||
| Solubility | Insoluble in water | ||
| GHS hazards[8] |    | ||
| R phrases | R26/27/28-R33-R50/53 | ||
| S phrases | (S1/2)-S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61 | ||
References
- ^ Record of CAS RN 25154-54-5 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ E. B. Starkey (1939). "Org. Synth". 19: 40. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.019.0040.
- ^ a b Record of CAS RN 528-29-0 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 11 March 2008.
- ^ a b Record of CAS RN 99-65-0 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 11 March 2008.
- ^ Record of CAS RN 100-25-4 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 11 March 2008.
- ^ a b c d Brockhaus ABC Chemie, VEB F.A. Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1971.
- ^ a b c d Félix-Rivera, Hilsamar (2011). "Triacetone triperoxide thermogravimetric study of vapor pressure and enthalpy of sublimation in 303–338K temperature range". Thermochimica Acta. 514 (1–2): 37–43. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2010.11.034.)
- ^ Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (Second revised ed.), New York and Geneva: United Nations, 2007, ISBN 978-92-1-116957-7, ST/SG/AC.10/30/Rev.2