 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4,5-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene | |
| Other names Xantphos | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.008 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C39H32OP2 |
| Molar mass | 578.62 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.34 g/mL |
| Melting point | 224 to 228 °C (435 to 442 °F; 497 to 501 K) |
| organic solvents | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
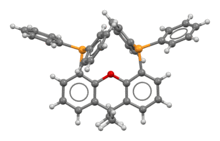
Xantphos is an organophosphorus compound derived from the heterocycle xanthene. It is used as a bidentate diphosphine ligand and is noteworthy for having a particularly wide bite angle (108°).[1] Such ligands are useful in the hydroformylation of alkenes.[2] Illustrative of its wide bite angle, it forms both cis and trans adducts of platinum(II) chloride. In the latter context, xantphos is classified as a trans-spanning ligand. A related bidentate ligand with a greater bite angle is spanphos.
The ligand is prepared by double directed lithiation of 9,9-dimethylxanthene with sec-butyllithium followed by treatment with chlorodiphenylphosphine.[3]
References
- ^ Birkholz, Mandy-Nicole; Freixa, Zoraida; van Leeuwen, Piet W. N. M. (2009). "Bite angle effects of diphosphines in C–C and C–X bond forming cross coupling reactions". Chemical Society Reviews. 38 (4): 1099–118. doi:10.1039/B806211K. PMID 19421583.
- ^ Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen, Paul C. J. Kamer, Joost N. H. Reek, and Peter Dierkes (2000). "Ligand Bite Angle Effects in Metal-catalyzed C-C Bond Formation". Chemical Reviews. 100 (8): 2741–2769. doi:10.1021/cr9902704. PMID 11749304.
- ^ Mirko Kranenburg, Yuri E. M. van der Burgt, Paul C. J. Kamer, Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen, Kees Goubitz, and Jan Fraanje (1995). "New Diphosphine Ligands Based on Heterocyclic Aromatics Inducing Very High Regioselectivity in Rhodium-Catalyzed Hydroformylation: Effect of the Bite Angle" (PDF). Organometallics. 14 (6): 3081–3089. doi:10.1021/om00006a057.