 Parties Signatories Non-parties | |
| Signed | August 22, 1978 |
|---|---|
| Location | Vienna |
| Effective | November 6, 1996 |
| Condition | 15 ratifications |
| Parties | 23[1] |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish |
| |
The Vienna Convention on Succession of States in respect of Treaties is an international treaty opened for signature in 1978 to set rules on succession of states. It was adopted partly in response to the "profound transformation of the international community brought about by the decolonization process". It entered into force on 6 November 1996, which was triggered by the succession of North Macedonia to the treaty giving it the requisite 15 parties.[1]
The treaty has proven to be controversial largely because it distinguishes between "newly independent states" (a euphemism for former colonies) and "cases of separation of parts of a state" (a euphemism for all other new states).
Article 16 states that newly independent states receive a "clean slate", such that the new state does not inherit the treaty obligations of the colonial power, whereas article 34(1) states that all other new states remain bound by the treaty obligations of the state from which they separated. Moreover, article 17 states that newly independent states may join multilateral treaties to which their former colonizers were a party without the consent of the other parties in most circumstances, whereas article 9 states that all other new states may only join multilateral treaties to which their predecessor states were a part with the consent of the other parties.
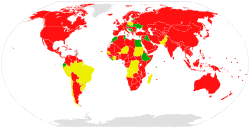
Parties to the convention
As of February 2019, there are 23 state parties which have ratified the convention. A further 14 states signed the convention but have not ratified it.[1]
List of parties
| State[1] | Signed | Deposited | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jul 22, 1993 | Succession from | ||
| Aug 23, 1978 | Feb 7, 2019 | ||
| Oct 22, 1992 | Succession from | ||
| Mar 12, 2004 | Accession | ||
| Feb 22, 1993 | Jul 26, 1999 | Ratification Succession to the signature of | |
| Jun 24, 1988 | Accession | ||
| Jul 25, 2006 | Accession | ||
| Jul 17, 1986 | Accession | ||
| Oct 21, 1991 | Accession | ||
| Aug 23, 1978 | May 28, 1980 | Ratification | |
| May 23, 1979 | Dec 5, 1979 | Ratification | |
| Sep 16, 2005 | Accession | ||
| Oct 7, 1996 | Succession from | ||
| Feb 9, 2009 | Accession | ||
| Oct 23, 2006 | Succession from | ||
| Mar 31, 1983 | Accession | ||
| Apr 27, 1999 | Accession | ||
| Mar 12, 2001 | Succession as | ||
| Feb 22, 1980 | Accession | ||
| May 28, 1993 | Apr 24, 1995 | Ratification Succession to the signature of | |
| Jul 6, 1992 | Succession from | ||
| Sep 16, 1981 | Accession | ||
| Oct 26, 1992 | Accession |
List of signatory states
| State[1] | Signed |
|---|---|
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Jan 10, 1979 | |
| Aug 31, 1979 | |
| Aug 30, 1978 | |
| Aug 16, 1979 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 | |
| Aug 23, 1978 |
See also
- Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (1969)
- Vienna Conventions
References
- ^ a b c d e "Vienna Convention on succession of States in respect of treaties". United Nations Treaty Series. 2013-07-26. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
