| Rectus sheath hematoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rectus abdominis muscle |
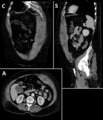
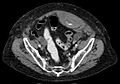
A rectus sheath hematoma is an accumulation of blood in the sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle. It causes abdominal pain with or without a mass.
The hematoma may be caused by either rupture of the epigastric artery or by a muscular tear. Causes of this include anticoagulation, coughing, pregnancy, abdominal surgery and trauma. With an ageing population and the widespread use of anticoagulant medications, there is evidence that this historically benign condition is becoming more common and more serious.[1]
On abdominal examination, people may have a positive Carnett's sign.
Most hematomas resolve without treatment, but they may take several months to resolve.
Rectus sheath hematoma as seen on ultrasound[2]
References
- ^ Fitzgerald, J. E. F.; Fitzgerald, L. A.; Anderson, F. E.; Acheson, A. G. (2009). "The changing nature of rectus sheath haematoma: Case series and literature review". International Journal of Surgery. 7 (2): 150–154. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2009.01.007. PMID 19261556.
- ^ "UOTW #13 - Ultrasound of the Week". Ultrasound of the Week. 12 August 2014. Retrieved 27 May 2017.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |