Pteridine 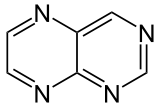 |
| |
| Names |
| IUPAC name pteridine |
| Identifiers |
| | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| | |
| UNII | |
| | |
InChI=1S/C6H4N4/c1-2-9-6-5(8-1)3-7-4-10-6/h1-4H  Key: CPNGPNLZQNNVQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N  InChI=1/C6H4N4/c1-2-9-6-5(8-1)3-7-4-10-6/h1-4H Key: CPNGPNLZQNNVQM-UHFFFAOYAU
|
| |
| Properties |
Chemical formula | C6H4N4 |
| Molar mass | 132.126 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 139.5 °C (283.1 °F; 412.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
| | |
Pteridine is an aromatic chemical compound composed of fused pyrimidine and pyrazine rings. A pteridine is also a group of heterocyclic compounds containing a wide variety of substitutions on this structure. Pterins and flavins are classes of substituted pteridines that have diverse biological roles.[1]
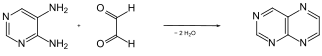
Synthesis of pteridine from 4,5-diaminopyrimidine and glyoxal
See also
References
- ^ Kritsky, M. S; Telegina, T. A; Vechtomova, Y. L; Kolesnikov, M. P; Lyudnikova, T. A; Golub, O. A (2010). "Excited flavin and pterin coenzyme molecules in evolution". Biochemistry. Biokhimiia. 75 (10): 1200–16. PMID 21166638.
This article is copied from an
article on Wikipedia® - the free encyclopedia created and edited by its online user community. The text was not checked or edited by anyone on our staff. Although the vast majority of Wikipedia® encyclopedia articles provide accurate and timely information, please do not assume the accuracy of any particular article. This article is distributed under the terms of
GNU Free Documentation License.
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.