Pidie Regency Kabupaten Pidie | |
|---|---|
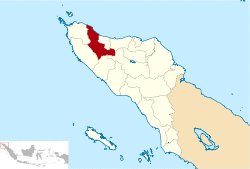 Location within Aceh | |
| Coordinates: 4°40′00″N 96°00′00″E / 4.66667°N 96°E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Region | Sumatra |
| Province | Aceh |
| Established | 1956 |
| Regency seat | Sigli |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Roni Ahmad |
| • Vice Regent | Fadhlullah T.M. Daud |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,562.14 km2 (1,375.35 sq mi) |
| Population (2016)[1] | |
| • Total | 425,974 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (IWST) |
| Area code | (+62) 653 |
| Website | pidiekab |
Pidie Regency (also known as: Pidie, Pědir;[2] "king of") is a regency of Aceh Special region, in Indonesia. It is located in the north of the island of Sumatra, in Western Indonesia, bordered by the Malacca Strait and Pidie Jaya Regency (which was formerly a part of Pidie Regency until it was separated out in 2007) in the north, Aceh Besar Regency in the west, Bireuen Regency in the northeast, and Aceh Jaya Regency in the south. The regency covers an area of 3,562.14 square kilometres and according to the 2010 census had a population of 379,108 people;[3] the latest official estimate (as at mid 2016) is 425,974.[4] Pidie was the largest rice-producing area of Aceh province, producing some 20% of its total output.
People from Pidie control various markets in Aceh special region, in the neighbouring province of North Sumatra (specifically its Medan City), and in the neighboring country of Malaysia. [5]
Administrative divisions
The regency is divided administratively into twenty-three districts (kecamatan), listed below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census,[6] together with the official estimates of their population for mid 2016.[7] The table also includes the number of administrative villages (desa and kelurahan) in each district, and its post code.
| Name | Area in km2[8] | Pop'n Census 2010[9] | Pop'n Census 2010[10] | No. of villages | Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geumpang | 594.64 | 6,008 | 6,731 | 5 | 24167 |
| Mane | 817.50 | 7,786 | 8,739 | 4 | 24189 |
| Geulumpang Tiga | 59.70 | 16,888 | 19,176 | 34 | 24183 |
| Glumpang Baro | 45.30 | 9,622 | 10,777 | 21 | 24180 |
| Mutiara | 35.05 | 18,418 | 20,810 | 29 | 24173 |
| Mutiara Timur (East Mutiara) | 63.55 | 30,767 | 34,340 | 48 | 24175 |
| Tiro (Truseb) | 255.00 | 7,097 | 7,925 | 19 | 24174 |
| Tangse | 750.00 | 23,509 | 26,235 | 28 | 24166 |
| Keumala | 27.57 | 8,905 | 9,915 | 18 | 24165 |
| Titeue | 20.11 | 6,101 | 6,898 | 13 | 24168 |
| Sakti | 70.03 | 18,817 | 21,421 | 49 | 24164 |
| Mila | 21.32 | 8,068 | 9,048 | 20 | 24163 |
| Padang Tiji | 258.71 | 19,633 | 21,959 | 64 | 24161 |
| Delima | 43.89 | 18,659 | 20,763 | 44 | 24161 |
| Grong Grong | 19.41 | 6,209 | 7,012 | 15 | 24150 |
| Iidrajaya | 34.02 | 20,715 | 23,263 | 49 | 24171 |
| Peukan Baro | 30.00 | 18,253 | 20,535 | 48 | 24172 |
| Kembang Tanjong | 46.50 | 19,315 | 21,738 | 45 | 24182 |
| Simpang Tiga | 55.36 | 20,291 | 22,919 | 52 | 24181 |
| Kota Sigli (Sigli town) | 9.75 | 18,829 | 21,366 | 15 | 24115 -24119 |
| Pidie (town) | 38.00 | 39,814 | 44,728 | 64 | 24151 |
| Batee | 104.74 | 18,077 | 20,249 | 28 | 24152 |
| Muara Tiga | 162.00 | 17,427 | 19,427 | 18 | 24153 |
| Totals | 3,562.14 | 379,108 | 425,974 | 730 |
Notable people
- Zaini Abdullah (governor of Aceh 2013 - 2018).
- Teungku Chik di Tiro (Indonesian National Hero).
- Daud Beureueh (Military Governor of aceh).
- Teuku Mohammad Hasan (The first governor of Sumatra).
- Ibrahim Hasan (former governor of Aceh and Former Minister for Food).
- Hasballah M Saad (Former minister of indonesian human rights).
- Hasan Tiro (Founder and command center of GAM).
- Sanusi Juned (Former chief minister of Malaysian).
- Ismail Hassan Metareum (Party chairman and Advisory specially Indonesian delegation to the UN).
- Ibrahim Risjad or Richard (influential businessmen in Indonesian).
References
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2020.
- ^ Ricklefs, M.C. (2008). History of Modern Indonesia Since c. 1200. Stanford University Press. p. 364.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2020.
- ^ The second five-year development plan, 1974/75-1978/79. Dept. of Information, Republic of Indonesia. 1977. p. 29. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2020.
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2016.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.