 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
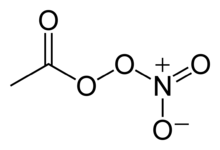
| IUPAC name nitroethaneperoxoate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name ethanoic nitric peroxyanhydride | |
| Other names PAN peroxyacetyl nitrate α-oxoethylperoxylnitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | PAN |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.187 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
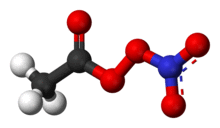
Chemical formula | C2H3NO5 |
| Molar mass | 121.05 g mol−1 |
| 1.46 × 10 5 mg l−1 at 298 K | |
| log P | −0.19 |
| Vapor pressure | 29.2 mmHg at 298 K |
Henry's law constant (kH) | 0.000278 m3 atm mol−1 at 298 K |
Atmospheric OH rate constant | 10−13 cm3 molecule−1 s−1 at 298 K |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Peroxyacetyl nitrate is a peroxyacyl nitrate. It is a secondary pollutant present in photochemical smog.[1] It is thermally unstable and decomposes into peroxyethanoyl radicals and nitrogen dioxide gas.[2] It is a lachrymatory substance, meaning that it irritates the lungs and eyes.[3]
Peroxyacetyl nitrate, or PAN, is an oxidant that is more stable than ozone. Hence, it is more capable of long-range transport than ozone. It serves as a carrier for oxides of nitrogen (NOx) into rural regions and causes ozone formation in the global troposphere.[1]
References
- ^ a b Singh, H.B. (2015). "TROPOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY AND COMPOSITION | Peroxyacetyl Nitrate". In North, Gerald R.; Pyle, John A.; Zhang, Fuqing (eds.). Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences. pp. 251–254. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-382225-3.00433-3. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3.
- ^ Finlayson-Pitts, Barbara J.; Pitts, James N. (2000). Chemistry of the Upper and Lower Atmosphere. ISBN 978-0-12-257060-5.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology. 2002. ISBN 978-0-12-227410-7.