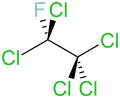
Pentachlorofluoroethane | |
| Names |
| IUPAC name 1,1,1,2,2-Pentachloro-2-fluoroethane |
| Other names Pentachloromonofluoroethane
CFC-111
R-111 |
| Identifiers |
| | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| | |
| | |
InChI=1S/C2Cl5F/c3-1(4,5)2(6,7)8  Key: KQKBWZDTYSQPMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N  InChI=1/C2Cl5F/c3-1(4,5)2(6,7)8 Key: KQKBWZDTYSQPMD-UHFFFAOYAV
|
| |
| Properties |
Chemical formula | C2Cl5F |
| Molar mass | 220.283 |
| Melting point | 101.5 °C (214.7 °F; 374.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
| | |
Pentachlorofluoroethane is a chlorofluorocarbon once used as a propellant and refrigerant. Its production and consumption has been banned since January 1, 1996 in developed countries, and January 1, 2010 in developing countries under the Montreal Protocol because of its ozone-depleting potential.[1]
References
External links
This article is copied from an
article on Wikipedia® - the free encyclopedia created and edited by its online user community. The text was not checked or edited by anyone on our staff. Although the vast majority of Wikipedia® encyclopedia articles provide accurate and timely information, please do not assume the accuracy of any particular article. This article is distributed under the terms of
GNU Free Documentation License.
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.
.gif)