 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name [4-[Bis(4-aminophenyl)methylidene]-1-cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene]dianiline | |
| Other names Pararosaniline p-rosaniline C.I. 42500 Para magenta | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.106.992 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
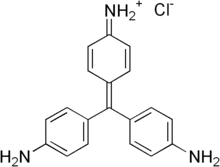
Chemical formula | C19H17N3 |
| Molar mass | 323.83 g/mol |
| Appearance | Green crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 268 to 270 °C (514 to 518 °F; 541 to 543 K) decomposes |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Pararosaniline, Basic Red 9, or C.I. 42500 is an organic compound with the formula [(H2NC6H4)3C]Cl. It is a magenta solid with a variety of uses as a dye.[1] It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine. (The others are rosaniline, new fuchsine and magenta II.)[2] It is structurally related to other triarylmethane dyes called methyl violets including crystal violet, which feature methyl groups on nitrogen.
It is prepared by the condensation of aniline and para-aminobenzaldehyde. Alternatively, it arises from the oxidation of 4,4'-bis(aminophenyl)methane in the presence of aniline.
Uses
- It is used to dye polyacrylonitrile fibers.
- Pararosaniline is used as a colorimetric test for aldehydes, in the Schiff test. It is the only basic fuchsine component suitable for making the aldehyde-fuchsine stain for pancreatic islet beta cells.[3]
- It has use as an Antischistosomal GB 908634 (1962 to Parke Davis & Co).
References
- ^ Thomas Gessner and Udo Mayer "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_179
- ^ Horobin RW, Kiernan JA (2002) Conn's Biological Stains, 10th ed. Oxford: BIOS.
- ^ Mowry, RW; Emmel, VM (1978). "Aldehyde fuchsin staining, direct or after oxidation: problems and remedies, with special reference to pancreatic B cells, pituitaries and elastic fibers". Stain Technology. 53: 141–154. doi:10.3109/10520297809111457.
Further reading
- Colour Index 3rd Edition Volume 4 (PDF), Bradford: Society of Dyers and Colourists, 1971, p. 4388, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-19.
- Gessner, T.; Mayer, U. (2002), "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 6th Edition, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_179.