 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tinset, others |
| Other names | KW-4354; McN-JR 35443; R-35443 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.637 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
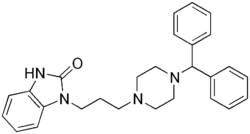
| Formula | C27H30N4O |
| Molar mass | 426.564 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Oxatomide, sold under the brand name Tinset among others, is a first-generation antihistamine of the diphenylmethylpiperazine family which is marketed in Europe, Japan, and a number of other countries.[1][2][3][4] It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1975.[5] Oxatomide lacks any anticholinergic effects.[2] In addition to its H1 receptor antagonism, it also possesses antiserotonergic activity similarly to hydroxyzine.[2]
It was patented in 1976 and came into medical use in 1981.[6]
Chemistry
Synthesis

Reaction of 2-Benzimidazolinone with isopropenyl acetate leads to the singly protected imidazolone derivative (2). Alkylation of this with 3-chloro-1-bromopropane affords the functionalized derivative (3). Alkylation of the monobenzhydryl derivative of piperazine (4) with 3 gives oxatomide (5), after hydrolytic removal of the protecting group.
References
- ^ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 912–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b c Ohmori K, Ishii H, Nito M, Shuto K, Nakamizo N (May 1983). "[Pharmacological studies on oxatomide (KW-4354). (7) Antagonistic effects on chemical mediators]". Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Folia Pharmacologica Japonica (in Japanese). 81 (5): 399–409. doi:10.1254/fpj.81.399. PMID 6138301.
- ^ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 768–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ "Oxatomide".
- ^ Harry Schwartz (August 1989). Breakthrough: the discovery of modern medicines at Janssen. Skyline Pub. Group. p. 149. ISBN 978-1-56019-100-1.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 548. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ J. Vandenberk et al., DE 2714437; eidem, U.S. Patent 4,250,176 (1977, 1981 both to Janssen).