 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
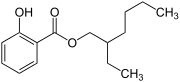
| IUPAC name 2-ethylhexyl 2-hydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names octisalate; 2-ethylhexyl salicylate; ethyl hexyl salicylate; 2-ethylhexyl ester salicylic acid; salicylic acid, 2-ethylhexyl ester; benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-ethylhexyl ester; 2-ethylhexyl ester benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-; 2-hydroxy- 2-ethylhexyl ester benzoic acid; | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.877 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C15H22O3 |
| Molar mass | 250.33 g/mol |
| Density | 1.014 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | < 25 °C (77 °F; 298 K) |
| Boiling point | 189 °C (372 °F; 462 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Octyl salicylate, or 2-ethylhexyl salicylate, is an organic compound used as an ingredient in sunscreens and cosmetics to absorb UVB (ultraviolet) rays from the sun.[1] It is an ester formed by the condensation of a salicylic acid with 2-ethylhexanol. It is a colorless oily liquid with a slight floral odor.
The salicylate portion of the molecule absorbs ultraviolet light, protecting skin from the harmful effects of exposure to sunlight. The ethylhexanol portion is a fatty alcohol, adding emollient and oil-like (water resistant) properties.
Notes
References
- "The Skin Cancer Foundation's Guide to Sunscreens". Skin Cancer Foundation. 2011. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
