| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
 Infrared image of the Cat's Paw Nebula. Green areas showing regions where radiation from hot stars collided with large molecules and small dust grains called "polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons" (PAHs), causing them to fluoresce Credit: Spitzer space telescope, 2018 | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 17 20 50.9h [1] |
| Declination | −36° 06′ 54″[1] |
| Distance | 5.54 ± 0.98 kly (1.7 ± 0.3 kpc)[2] ly |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 40'×23' |
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 40 ly |
| Designations | NGC 6334, ESO 392-EN 009,[3] Sharpless 8, RCW 127, Gum 64 |
NGC 6334, colloqually known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, Bear Claw Nebula, or Gum 64, is an emission nebula and star-forming region located in the constellation Scorpius.[4] It was discovered by astronomer John Herschel in 1837, who observed it from the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa.[5] The nebula is located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way,[6] at a distance of approximately 5.5 kilolight-years from the Sun[2]
The nebula is a high mass filamentary cloud structure spanning ~320 ly. Several embedded star-forming regions have been identified from infrared and radio emissions. Four of these sites have formed H II regions.[6]
Gallery
VLT Survey Telescope image shows the Cat's Paw Nebula and the Lobster Nebula [7]
This portrait of NGC 6334 was created from images taken with the Wide Field Imager instrument at the 2.2-metre MPG/ESO telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile.
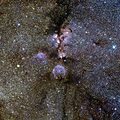
Protocluster NGC 6334I is a star-forming cloud in the Cat's Paw Nebula.[8]
References
- ^ a b Kharchenko, N. V.; et al. (2013), "Global survey of star clusters in the Milky Way. II. The catalogue of basic parameters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 558: 8, arXiv:1308.5822, Bibcode:2013A&A...558A..53K, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322302, A53.
- ^ a b Russeil, D.; et al. (2012). "Statistical study of OB stars in NGC 6334 and NGC 6357". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 538: A142. Bibcode:2012A&A...538A.142R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117299.
- ^ "NGC 6334". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2007-04-10.
- ^ Nemiroff, R.; Bonnell, J., eds. (2003-07-17). "The Cat's Paw Nebula". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. Retrieved 2007-11-05.
- ^ "NGC 6334 - The Cat's Paw Nebula". SEDS Database. SEDS. Retrieved 2008-04-15.
- ^ a b Sadaghiani, M.; et al. (March 2020). "Physical properties of the star-forming clusters in NGC 6334. A study of the continuum dust emission with ALMA". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 635: 25. arXiv:1911.06579. Bibcode:2020A&A...635A...2S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935699. A2.
- ^ "The Cat's Paw and Lobster Nebulae". www.eso.org. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- ^ "Protostar blazes and reshapes its stellar nursery". www.eso.org. Retrieved 20 March 2017.
External links
- On the Trail of a Cosmic Cat — ESO Photo Release
- NGC 6334 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- Astronomy Picture of the Day - Wide Angle: The Cat's Paw Nebula 2010 April 21
- Cat's Paw Nebula at Constellation Guide