 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Propan-2-yl acetate | |
| Other names Isopropyl acetate 2-Acetoxypropane 2-Propyl acetate 2-Propyl ethanoate Propan-2-yl ethanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.238 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C5H10O2 |
| Molar mass | 102.133 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.87 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −73 °C (−99 °F; 200 K) |
| Boiling point | 89 °C (192 °F; 362 K) |
| 4.3 g/100 mL (27 °C) | |
| Vapor pressure | 42 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
| −67.04·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R11, R36, R66, R67 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2), S16, S26, S29, S33 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 2 °C (36 °F; 275 K) |
Autoignition temperature | 460 °C (860 °F; 733 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.8–7.8% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration) | 11,918 ppm (rat, 8 hr)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) | TWA 250 ppm (950 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended) | None established[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) | 1800 ppm[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
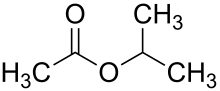
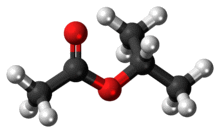
Isopropyl acetate is an ester, an organic compound which is the product of esterification of acetic acid and isopropanol. It is a clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic fruity odor.[3]
Isopropyl acetate is a solvent with a wide variety of manufacturing uses that is miscible with most other organic solvents, and moderately soluble in water. It is used as a solvent for cellulose, plastics, oil and fats. It is a component of some printing inks[4] and perfumes.
Isopropyl acetate decomposes slowly on contact with steel in the presence of air, producing acetic acid and isopropanol. It reacts violently with oxidizing materials and it attacks many plastics.[5]
Isopropyl acetate is quite flammable in both its liquid and vapor forms, and it may be harmful if swallowed or inhaled.[6]
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL) of 250 ppm (950 mg/m3) over an eight-hour time-weighted average for workers handling isopropyl acetate.[7]
References
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0358". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Isopropyl acetate". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Isopropyl acetate". ChemViP.
- ^ "Celanese - The chemistry inside innovation™". chemvip.com. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ "ISOPROPYL ACETATE". International Chemical Safety Cards. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2009-06-25.
- ^ "Iso-propyl Acetate". Material Safety Data Sheets.
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - Isopropyl acetate". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
