 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High (rapid and complete absorption) |
| Metabolism | Glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 2.3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
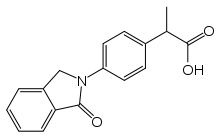
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.197 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 281.311 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Indoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It was withdrawn worldwide in the 1980s after postmarketing reports of severe gastrointestinal bleeding.[1]
A 2004 study using high-throughput screening found indoprofen to increase production of the survival of motor neuron protein, suggesting it may provide insight into treatments for spinal muscular atrophies.[1][2]
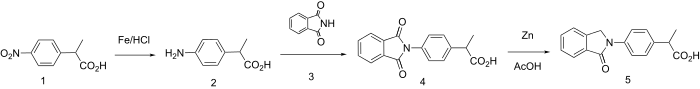
Synthesis
The isoindolone ring system forms the nucleus for one of the more traditional "profen" NSAIDs.
Reduction of the nitro group in arylpropionic acid (1) gives the corresponding aniline (2). Reaction of the intermediate with the imide (3) from phthalic anhydride (i.e. phthalimide) gives the product (4) in which the aniline nitrogen has exchanged with ammonia (apparently phthalic anhydride was not used directly). Treatment of the new imide with zinc in acetic acid leads to reduction of but one of the carbonyl groups to afford indolone, indoprofen.
References
- ^ a b Frazin N (March 9, 2005). "Pain Reliever May Provide Clues for Treating Spinal Muscular Atrophy". United States National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ Lunn MR, Root DE, Martino AM, Flaherty SP, Kelley BP, Coovert DD, et al. (November 2004). "Indoprofen upregulates the survival motor neuron protein through a cyclooxygenase-independent mechanism". Chemistry & Biology. 11 (11): 1489–93. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.08.024. PMC 3160629. PMID 15555999.
- ^ Nannini G, Giraldi PN, Molgora G, Biasoli G, Spinelli F, Logemann W, et al. (August 1973). "New analgesic-anti-inflammatory drugs. 1-Oxo-2-substituted isoindoline derivatives". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 23 (8): 1090–100. doi:10.1002/chin.197344288. PMID 4801034.
- ^ BE 753600; Carney RW, de Stevens G U.S. Patent 4,316,850 (1970, 1982 both to Ciba).
- ^ Giraldi PN, et al., DE 2154525 (1972 to Carlo Erba), C.A. 77, 88292v (1972).