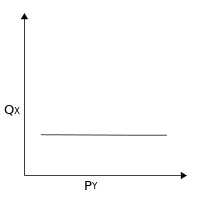
Independent goods are goods that have a zero cross elasticity of demand. Changes in the price of one good will have no effect on the demand for an independent good. Thus independent goods are neither complements nor substitutes.
For example, a person's demand for nails is usually independent of his or her demand for bread, since they are two unrelated types of goods. Note that this concept is subjective and depends on the consumer's personal utility function.
A Cobb-Douglas utility function implies that goods are independent. For goods in quantities X1 and X2, prices p1 and p2, income m, and utility function parameter a, the utility function
when optimized subject to the budget constraint that expenditure on the two goods cannot exceed income, gives rise to this demand function for good 1:[1] which does not depend on p2.
See also
References
- ^ R Varian, Hal (2006). Intermediate Microeconomics : A modern approach 7th Edition. W.W. Norton & Co. p. 754. ISBN 0-393-92702-4.