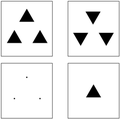
In chemistry and crystallography, crystal structures that have the same set of interatomic distances are called homometric structures.[1] Homometric structures need not be congruent (that is, related by a rigid motion or reflection). Homometric crystal structures produce identical diffraction patterns; therefore, they cannot be distinguished by a diffraction experiment.
Recently, a Monte Carlo algorithm was proposed to calculate the number of homometric structures corresponding to any given set of interatomic distances.[2]
See also
Notes
- ^ Patterson, A.L. (1939). "Homometric Structures". Nature. 143 (3631): 939–940. Bibcode:1939Natur.143..939P. doi:10.1038/143939b0.
- ^ Gommes C.J.; Jiao Y; Torquato S (2012). "Density of States for a Specified Correlation Function and the Energy Landscape". Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 (8): 080601. arXiv:1201.1142. Bibcode:2012PhRvL.108h0601G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.080601. PMID 22463509.