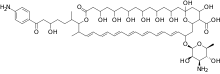
Hamycin is a pair polyene antimycotic organic compounds described in India.[1] It is a heptaene antifungal compound rather similar in chemical structure to amphotericin B except that it has an additional aromatic group bonded to the molecule. When pure, hamycin is a yellow, powdered solid. There are two versions of hamycin with very similar chemical structures: hamycin A and hamycin B.[2]
Sources
Hamycin is obtained from a strain of streptomyces bacteria growing in soil i.e., Streptomyces pimprina. This compound is being produced in India by Hindustan Antibiotics Limited, located at Pimpri, Pune, Maharashtra, India. It is similar to nystatin and it is more water-soluble.
Uses
It is useful as an antifungal antibiotic drug for topical as well as systemic mycoses.
References
- ^ Aggregation behaviour of hamycin and its interaction with membrane sterols
- ^ Kotler-Brajtburg, J; Medoff, G; Kobayashi, GS; Boggs, S; Schlessinger, D; Pandey, RC; Rinehart, KL Jr. "Classification of polyene antibiotics according to chemical structure and biological effects". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 15: 716–22. doi:10.1128/aac.15.5.716. PMC 352743. PMID 393163.