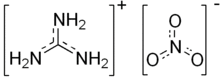 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Guanidinium nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.328 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 122.1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.436 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 216 °C (421 °F; 489 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes commencing at 240 °C |
| 160 g/l at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R20 R21 R22 R36 R38 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
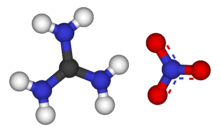
Guanidine nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula [C(NH2)3]NO3. It is a colorless, water-soluble salt. It is produced on a large scale and finds use as precursor for nitroguanidine,[1] fuel in pyrotechnics and gas generators. Its correct name is guanidinium nitrate, but the incorrect term guanidine nitrate is widely used.
Production and properties
Although it is the salt formed by neutralizing guanidine with nitric acid, guanidine nitrate is produced industrially by the reaction of dicyandiamide (or calcium salt) and ammonium nitrate.[2]
It has been used as a monopropellant in the Jetex engine for model airplanes. It is attractive because it has a high gas output and low flame temperature. It has a relatively high monopropellant specific impulse of 177 seconds (1.7 kN·s/kg).[note 1]
Guanidine nitrate's explosive decomposition is given by the following equation: H6N4CO3 (s) → 3 H2O (g) + 2 N2 (g) + C (s)
Safety
The compound is a hazardous substance, being an explosive and containing an oxidant (nitrate). It is also harmful to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract.[2]
Notes
- ^ 1000 lbf/in2 (700 kPa) chamber pressure, 14.7 lbf/in2 (101 kPa) exit pressure, shifting equilibrium theoretical performance.
- ^ E.-C. Koch, Insensitive High Explosives: III. Nitroguanidine - Synthesis - Structure - Spectroscopy- Sensitiveness, Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019, 44, 267-292.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/prep.201800253
- ^ a b Thomas Güthner, Bernd Mertschenk and Bernd Schulz "Guanidine and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_545.pub2
External links
- Jetex: Propellants
- PhysChem: Guanidine Nitrate MSDS
