| Gewald reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Karl Gewald |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | gewald-reaction |
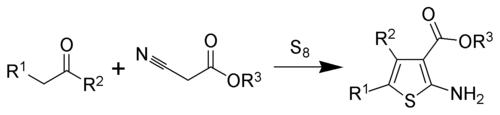
The Gewald reaction is an organic reaction involving the condensation of a ketone (or aldehyde when R2 = H) with a α-cyanoester in the presence of elemental sulfur and base to give a poly-substituted 2-amino-thiophene.[1][2]
The reaction is named after the German chemist Karl Gewald (born 1930).[3][4][5]
Reaction mechanism
The reaction mechanism of the Gewald reaction was elucidated 30 years after the reaction was discovered.[6] The first step is a Knoevenagel condensation between the ketone (1) and the α-cyanoester (2) to produce the stable intermediate 3. The mechanism of the addition of the elemental sulfur is unknown. It is postulated to proceed through intermediate 4. Cyclization and tautomerization will produce the desired product (6).
Microwave irradiation has been shown beneficial to reaction yields and times.[7]
Variations
In one variation of the Gewald reaction a 3-acetyl-2-aminothiophene is synthesized starting from a dithiane (an adduct of sulfur and acetone if R = CH3 or acetaldehyde if R = H) and the sodium salt of cyanoacetone which in itself is very unstable:[8]
References
- ^ Gewald, K.; Schinke, E.; Böttcher, H. Ber. 1966, 99, 94-100.
- ^ Sabnis, R. W. Sulfur Rep. 1994, 16, 1-17. (Review)
- ^ John A. Joule, Keith Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 5. Auflage (2010), p. 340, ISBN 978-1-4051-3300-5.
- ^ Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frank G. Favaloro, Jr.: Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, 2. Auflage (2005) p. 306, ISBN 0-471-22854-0.
- ^ Christopher Hume: Applications of Multicomponent Reactions in Drug Discovery – Lead Generation to Process Development, p. 311−341, see p. 332−334, In Jieping Zhu, Huges Bienaymé: Multicomponent Reactions, Wiles-VCH Verlag, 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-30806-4.
- ^ Sabnis, R. W.; Rangnekar, D. W.; Sonawane, N. D. J. Heterocyclic Chem. 1999, 36, 333.
- ^ Sridhar, M.; Raoa, R. M.; Babaa, N. H. K.; Kumbhare, R. M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 3171-3172. (doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.03.052)
- ^ Gernot A. Eller, Wolfgang Holzer Molecules 2006, 11, 371-376 Online article.