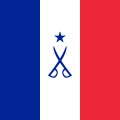
French Empire Empire français | |
|---|---|
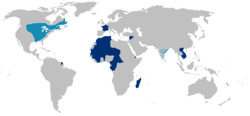 Flags were used to represent various territories and colonies across the Empire |
| List of French flags |
|---|
 |
| French ensigns |
| Regional flags |
| Flags of Île-de-France |
| Former French Empire |
Some of the colonies, protectorates and mandates of the French Colonial Empire used distinctive colonial flags. These most commonly had a French Tricolour in the canton.
As well as the flags of individual colonies, the governors-general of French colonies flew a square flag with a blue field and the French ensign in the canton. This flag was flown beneath the national ensign. Colonial governors used a rectangular swallow-tailed version of this flag.
Colonial flags with a tricolour canton
The flags with the French flag in the canton, which on many occasions were already existing flags without the tricolour, resembled the British colonial flags, which originated as defacements of the British ensigns, which have the British Union Jack in the canton, and a red, white or blue fly. Naval sources show flags such as those used in the French Mandate of Syria as having the tricolour with unequal stripes, as in the French ensign, but it is likely that these versions of the flags were used at sea, and on land the tricolour had the standard equal stripes.
While for the sake of simplicity French colonial ensign are on this page classified by appearance, this should not be taken to imply common origins or the existence of undefaced ensigns used by the French government unless otherwise noted.
Red field
- Laos, French Indochina: Laos was part of French Indochina from 1893. The tricolour was added to the flag of the Kingdom of Luang Prabang, which was red with a white image of a three headed elephant on a stand with a parasol.
- Morocco: The Protectorate of Morocco from 1919 to 1953, used the national flag with a tricolour in the canton as a civil ensign.
- Tunisia: From 1881–1956, Tunisia was a French protectorate. It has been reported that the tricolour was added to the Tunisian flag for use as a civil ensign, as in Morocco, but it seems that such a flag was never official.
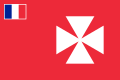
- Wallis and Futuna: The unofficial, but commonly used flag of Wallis and Futuna is red with four white triangles arranged in a square and the tricolour in the canton with a white fimbriation.
Blue field
- Damascus: This part of the French Mandate of Syria from 1922–25 used a blue flag with a white disk in the centre and the tricolour in the canton.
- Syria (1920): The French Mandate of Syria may have originally used a sky blue flag with a white crescent and star and French tricolour in the canton.
- In 1939, the governor-general's flag, was a square blue flag with a French ensign in the canton. With a swallow-tail, this flag was the colonial governors' flag.
White field
- Aleppo: This part of the French Mandate of Syria from 1920–25 used a white flag with tricolour in the canton and three yellow five-pointed stars in a triangle in the fly.
- Latakia: This part of the French Mandate of Syria used a white flag, ratio 2:3, with the tricolour in the canton taking up 1/9 of the area of the flag, red triangles in the other three corners, and a golden sunburst in the centre of the flag.
- The first banner of the French Revolution had a white field with a tricolour in the canton, although the order of the colours has since been reversed.
Green field
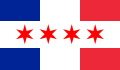
- Togo: The flag used in 1957–8 had two white five-pointed stars in the green field, one at the lower left-hand corner, the other in the upper right-hand corner.
Yellow field
- Annam, part of the Union of French Indochina from 1886 until 1954, used a flag with a plain yellow background, in two shapes one with the ratio 2:3 and the other 1:1 (square).
Multicolour field
- Jebel Druze. From 1924 until 1936, this part of the French Mandate of Syria had a flag with a white vertical strip beneath the tricolour in the canton, with the rest of the flag made up of green, red, yellow, blue and white horizontal stripes.
- Syria: In 1922, the French Mandate was made a federation, with a federal flag made up of green-white-green horizontal stripes and the tricolour in the canton. This flag was also used when Aleppo and Damascus merged.
Colonial flags with other designs
Modified tricolours
- Lebanon: The French Mandate of Greater Lebanon (1920–43) used as a flag the French tricolour with a green cedar in the middle stripe. See picture in "Flag of Lebanon - History"
Other designs
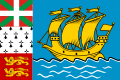
- French Polynesia: The flag of French Polynesia has the horizontal stripes, red-white-red. The white stripe is twice the height of each red stripe, and contains an emblem consisting of a boat, the sun, and waves.
Galleries
Historical flags
Flag of the Autonomous Republic of Togo (1957-1958)
Flag of the French Senegal (1958-1959)
Flag of Gabon (1959-1960)
Flag of the French Mandate of Syria (organized into five states (Sanjak of Damascus, Sanjak of Aleppo, Alawite State, Sanjak of Latakia, the Jebel Druze, Greater Lebanon) (1920-1922)
Flag of the State of Alawites, later Sanjak of Latakia, in the French Mandate of Syria (1920-1936)
Flag of Jabal ad-Druze, in the French Mandate of Syria (1924-1936)
Flag of Madagascar, in the French Protectorate (1885-1895)
French Merchant Flag in the French Morocco (1919-1956)
Flag of Vanuatu under the Anglo-French Joint Naval Commission (1887-1906)
Flag of Tahiti under the Protectorate of France (1842-1880)
Flag of the State of Greater Lebanon during the French mandate (1920–1946)
Flag of the Tay people (1947-1954)
Flag of the French Protectorate of Wallis and Futuna (Uvea) (1860-1886)
Flag of the French Colony of French Sudan (1958-1959)
Proposed Flag of the French Congo (1959)
Flag of the French Saar (protectorate) (1947-1956)
Flag of the French protectorate of Rurutu in French Polynesia (1889-1900)
Flag of French protectorate of Rimatara (French Polynesia)(1891-1900)
Flag of French Protectorate of Raiatea (French Polynesia) (1880-1897)
Algerian ensign under the French rule (1848-1910)[1]
Flag of French Protectorate of Wallis and Futuna (1886-1887)
Flag of French Protectorate of Wallis and Futuna (1887-1910)
Flag of French Protectorate of Wallis and Futuna (1910-1958)
Flag of French Protectorate of Wallis and Futuna (1958-1985)
Flag of the Administrator of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (1958-2005)
Flags with French history
Flag of Acadia
Flag of the Franco-Albertan
Flag of the Acadians in New England
Flag of the Acadiana
Personal standard of Marshal Philippe Pétain as "Chief of State" of Vichy France
Flag of Pied-noir (2008-)
Unofficial flag of "French of Algeria" (Pied-Noir)
Flag of Louisiana in 1861
Flag of state of Minnesota with the French motto "L'Étoile du Nord"
Flag of the City of Detroit
Flag of Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Flag of Republic of Independent Guyana (1886-1887)
Louisville, Kentucky's flag (1949-2003)
Current official and unofficial flags of French overseas regions, collectivities and territories
Flag of the Administrator of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (2005-present)
Unofficial flag of Mayotte
Second official flag of New Caledonia
Unofficial flag of Saint Barthélemy
Current subnational flags of overseas collectivities and territories
Flag of Alo
Flag of Sigave
Flag of the Leeward Islands
Flag of the Tuamotu Archipelago
Flag of Rapa (French Polynesia) (nowadays)
Other official flags
Jack of the Minister of Overseas France
Jack of the Prime Minister
Jack of the Minister of Defence
Jack of an admiral
Jack of a Vice-amiral d'escadre
Jack of a vice-amiral
Jack of a contre-amiral
See also
- French colonial empires
- List of French flags
- List of French possessions and colonies
References
- F.E. Hulme, The Flags of the World: Their History, Blazonry, and Associations, From the Banner of the Crusader to the Burgee of the Yachtsman; Flags National, Colonial, Personal; The Ensigns of Mighty Empires; the Symbols of Lost Causes (Colonial Edition), Frederick Wayne and Co., London, pp. 152, (1895).
- W.J. Gordon, Flags of the World Past and Present: Their Story and Associations, Frederick Wayne and Co., Ltd., London, pp. 265, (1929).
- B. McCandless, and G. Grosvenor, "Our Flag Number", The National Geographic Magazine, National Geographic Society, Washington, D.C., Vol. XXXII, No. 4, pp. 420, October, (1917).
- G. Grosvenor, and W.J. Showalter, "Flags of the World", The National Geographic Magazine, National Geographic Society, Washington, D.C., Vol. LXVI, No. 3, pp. 338–396, September, (1934).
- Flags of All Nations Volume I. National Flags and Ensigns (B.R.20(1) 1955), Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, (1955).
- Flags of All Nations Volume II. Standards of Rulers, Sovereigns and Heads of State; Flags of Heads of Ministries, and of Naval, Military, and Air Force Officers (B.R.20(2) 1958), Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, (1958).
- Flags of All Nations Change Five (BR20), Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, (1989), Revision (1999).
- W. Smith, Flags Through the Ages and Across the World, McGraw-Hill Book Co., Ltd., Maidenhead, England, pp. 361, (1975).
- J.W. Norie, and J.S. Hobbs, Three Hundred and Six Illustrations of the Maritime Flags of All Nations; Arranged Geographically, with Enlarged Standards: Together with Regulations and Instructions Relating to British Flags &c., Printed for, and Published by C. Wilson, At the Navigation Warehouse and Naval Academy, No. 157, Leadenhall Street, Near Cornhill,(Facsimile reprint of 1848 original), (1987).
- Ottfried Neubecker, Flaggenbuch (Flg.B.). Bearbeitet und herausgegeben vom Oberkommando der Kriegsmarine. Abgesclossen am 1. December 1939, (Historical Facsimile edition containing all national and international flags 1939-1945), pp. 193, (1992).

.svg.png)



.svg.jpg)
.svg.gif)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)


.svg.png)




.svg.png)
.svg.png)








.svg.png)

.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.png)

.png)
.svg.png)


.gif)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)

.gif)












.svg.png)

.svg.png)

.svg.png)

.png)




.svg.png)




_variant.svg.gif)

.svg.jpg)

.svg.png)
.svg.jpg)






.svg.png)
_(actuel).gif)