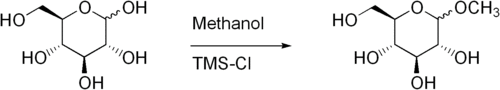
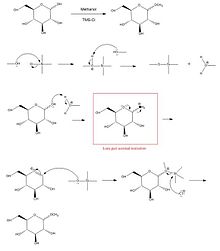
Fischer glycosidation (or Fischer glycosylation) refers to the formation of a glycoside by the reaction of an aldose or ketose with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction is named after the German chemist, Emil Fischer, winner of the Nobel Prize in chemistry, 1902, who developed this method between 1893 and 1895.[1][2][3]
Commonly, the reaction is performed using a solution or suspension of the carbohydrate in the alcohol as the solvent. The carbohydrate is usually completely unprotected. The Fischer glycosidation reaction is an equilibrium process and can lead to a mixture of ring size isomers, and anomers, plus in some cases, small amounts of acyclic forms. With hexoses, short reactions times usually lead to furanose ring forms, and longer reaction times lead to pyranose forms. With long reaction times the most thermodynamically stable product will result which, owing to the anomeric effect, is usually the alpha anomer.
See also
- Fischer–Speier esterification - a more general reaction where an alcohol and carboxylic acid are coupled to form an ester
- Helferich method - a glycosidation carried out with phenol [5]
References
- ^ Emil Fischer (1893). "Ueber die Glucoside der Alkohole". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 26 (3): 2400–2412. doi:10.1002/cber.18930260327.
- ^ Emil Fischer; Leo Beensch (1894). "Ueber einige synthetische Glucoside". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 27 (2): 2478–2486. doi:10.1002/cber.189402702248.
- ^ Emil Fischer (1895). "Ueber die Verbindungen der Zucker mit den Alkoholen und Ketonen". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 28 (1): 1145–1167. doi:10.1002/cber.189502801248.
- ^ Izumi, Minoru; Fukase, Koichi; Kusumoto, Shoichi (2002). "TMSCl as a mild and effective source of acidic catalysis in Fischer glycosidation and use of propargyl glycoside for anomeric protection". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 66 (1): 211–214. doi:10.1271/bbb.66.211. PMID 11866111.
- ^ Eine neue Methode zur Synthese von Glykosiden der Phenole1). (p 378-383) Burckhardt Helferich, Ernst Schmitz-Hillebrecht Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft Volume 66 Issue 3 , Pages 321 - 462 1933 doi:10.1002/cber.19330660313