Evros Περιφερειακή ενότητα Έβρου | |
|---|---|
Regional unit | |
 | |
 Evros within Greece | |
| Coordinates: 41°10′N 26°05′E / 41.167°N 26.083°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Region | East Macedonia and Thrace |
| Capital | Alexandroupoli |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,242 km2 (1,638 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 147,530[1] |
| Time zone | UTC+2 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal codes | 68x xx |
| Area codes | 255x0 |
| ISO 3166 code | GR-71 |
| Car plates | ΕΒ, ΟΡ |
Evros (Greek: Περιφερειακή ενότητα Έβρου) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace. Its name is derived from the river Evros, which appears to have been a Thracian hydronym. Evros is the northernmost regional unit. It borders Turkey to the east, across the river Evros, and it borders Bulgaria to the north and the northwest. Its capital is Alexandroupoli. Together with the regional units Rhodope and Xanthi, it forms the geographical region of Western Thrace. The population density was 34.77 per km2 (2011).
Geography
.svg.png)
Evros is one of the largest regional units of Greece. It forms the eastern part of the geographical region Western Thrace, and includes the island Samothrace in the northern Aegean Sea. Its length is about 150 km from north to south (excluding Samothrace). Its width ranges from 70 to 100 km from east to west. The most important rivers are the Evros and its tributary Arda.
The Rhodope Mountains lie in the west and the southwest. The Aegean Sea lies to the south. The Evros valley is flat. Samothrace is mountainous.
The coastal area has a predominantly Mediterranean climate, whereas the northern part and the mountains have a colder continental climate.
Administration
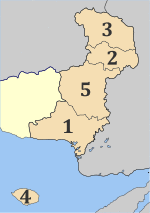
The Evros regional unit is subdivided into 5 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox):[2]
- Alexandroupoli (1)
- Didymoteicho (2)
- Orestiada (3)
- Samothrace (Samothraki, 4)
- Soufli (5)
Prefecture
Evros was established as a prefecture in 1930 (Greek: Νομός Έβρου), when the former Thrace Prefecture was divided into the Rhodope and Evros prefectures.[3] As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the prefecture was transformed into a regional unit within the East Macedonia and Thrace region, with no change in its boundaries. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.[2]
| New municipality (2011) | Old municipalities | Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Alexandroupoli | Alexandroupoli | Alexandroupoli |
| Traianoupoli | ||
| Feres | ||
| Didymoteicho | Didymoteicho | Didymoteicho |
| Metaxades | ||
| Orestiada | Orestiada | Orestiada |
| Vyssa | ||
| Kyprinos | ||
| Trigono | ||
| Samothrace (Samothraki) | Samothrace | Samothrace |
| Soufli | Soufli | Soufli |
| Orfeas | ||
| Tychero |
Provinces
- Province of Orestiada - Orestiada
- Province of Didymoteicho - Didymoteicho
- Province of Soufli - Soufli
- Province of Alexandroupoli - Alexandroupolis
- Province of Samothrace - Samothrace
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece.
History
As a part of Western Thrace, the territory of the Evros regional unit followed the fate of that region. At 1821, several parts of Evros region, such as Lavara and Samothraki rebelled, participated in the Greek War of Independence. It became part of Greece in 1920, when it was ceded by Bulgaria as a result of the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine. Initially it was part of the Thrace Prefecture, which was subdivided in 1930. During the Greco-Turkish War (1919-1922), many Greek refugees settled in the Evros, and new towns were built, including Orestiada. The Evros river valley was flooded several times, notably in 1997, 2005, and 2006.
Transport
The main roads in the Evros regional unit are:
- Egnatia Odos/E90 motorway (... Komotini - Alexandroupoli - İpsala (Turkey))
- Greek National Road 2 (... Komotini - Alexandroupoli - Feres)
- Greek National Road 51/E85 (Svilengrad (Bulgaria) - Orestiada - Didymoteicho - Feres)
- Greek National Road 53 (Ormenio - Metaxades - Aisymi - Alexandroupoli)
A railway line connects Alexandroupoli with Thessaloniki via Komotini, Xanthi and Drama. Another line connects Alexandroupoli with Dimitrovgrad, Bulgaria via Didymoteicho and Orestiada, with a branch line from Didymoteicho to Uzunköprü, Turkey.
The Alexandroupolis International Airport is served by mostly national flights.
Sights
The most important sights of the prefecture are:
- Church of Theotokos Kosmosoteira. The church was founded in 1152. It is considered one of the best examples of Byzantine art in Greece.
- Samothrace with the Sanctuary of the Great Gods and its Archaeological Museum.
- Evros Delta National Park
- Lighthouse of Alexandroupoli
- The post-Byzantine churches in the villages of Alepochori (Church of Saint Athanasius), Metaxades (Church of Saint Athanasius) and Paliouri (Church of Saint Pantaleon)
- The ancient Mesimvria-Zoni
- Dadia Forest
- Fossilized Forest of Lefkimmi
- Cyclops Polyphemus Cave in Makri
- Burial Tomb of Mikri Doxipara: Roman Tomb which dates from the 2nd century
- Didymoteicho
- Byzantine Castle
- Çelebi Sultan Mehmed Mosque
- Hamam of Oruç Paşa
- Türbe of Oruç Pasha
- the Kayali Cave and the Vouva Cave
- Castle of Pythio
- The thermal baths of Traianoupoli
- Castle of Avanta-Potamos
- The Ethnological Museum of Thrace in Alexandroupoli
- The Silk Museum of Soufli
- Zourafa islet
- The village Metaxades with its traditional architecture
- The Pomak villages Goniko and Roussa with the traditional architecture
Notable people
- Hrysopiyi Devetzi (1976, Alexandroupoli), Greek silver Olympic Champion in triple jump (Athens, 2004)
- Demis Nikolaidis (1973, Alexandroupoli), Greek international footballer, European Champion with Greek National team (Portugal, 2004)
- Stelios Venetidis (1976, Orestiada),Greek international footballer, European Champion with Greek National team (Portugal, 2004)
- Athanasios Tsigas (1982, Aristeino Alexandroupolis), Greek footballer
- Lefteris Hapsiadis (1953, Kila Feres), Greek lyricist and writer
- Andreas Andreadis (1982, Provatonas Soufli), Greek international volleyball player
- Marios Giourdas (1973, Alexandroupoli), international volleyball player
- Thanassis Moustakidis (1962, Soufli), Greek international volleyball player, player with the most appearances with Greek National team
- Nikos Samaras (1970-2013, Orestiada), Greek international volleyball player, player-symbol for the Greek volleyball
- Constantin Carathéodory (1873-1950, Nea Vyssa), Greek mathematician
- Dimosthenis Michalentzakis (1998, Feres), Greek Gold Paralympic Champion Swimmer in category S9 (Rio, 2016)
- Marinos Ouzounidis (1968, Alexandroupoli), former international Greek footballer, now football coach
- Manolis Siopis (1994, Alexandroupoli), Greek international footballer
- Dimosthenis Magginas (1982, Alexandroupoli), Greek middle-distance, long-distance runner
- Fotis Kosmas, (1926-1995), Alexandroupoli) Mediterranean and 7th Olympic winner in decathlon
- Kostas Gatsioudis (1973, Didymoteicho), 6th Olympic winner, Mediterranean and Silver World champion, in Javelin throw
- Nikos Alavantas (1959, Krios Orestiada), former Greek international footballer
- Giannis Matzourakis (1949, Didymoteicho), former footballer, now football coach
- Nikos Hadjinikolaou (1962, Alexandroupoli), Greek journalist
- Renos Haralampidis (1970, Spilaio), Greek actor, film director
- Yannis Stankoglou (1974, Thourio), Greek actor
- John III Doukas Vatatzes (1192–1254, Didymoteicho), emperor of Nicaea
- John V Palaiologos (1332–1391, Didymoteicho), Byzantine Emperor
- Bayezid II (1481–1512, Didymoteicho) Sultan of the Ottoman Empire
- Eugenios Eugenidis (1882–1954, Didymoteicho), shipping magnate
- Sürmeli Ali Pasha, (1645-1695, Didymoteicho), Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire
- Konstantinos Malamatinas, founder of retsina Malamatina[4]
- Paraskevas Tselios (1997, Alexandroupoli), Greek international volleyball player
- Savvas Gentsoglou (1990, Alexandroupoli), Greek football player
- Gregoris Mentzas (1960, Alexandroupoli), Greek management scientist and professor at the National Technical University of Athens
- Giorgos Valavanidis (1974, Alexandroupoli), Greek former basketball player, silver medalist with Greek National team U16 in 1991 and Greek champion with PAOK
- Arete Kosmidou (1997, Alexandroupoli), Greek singer
- Anestis Dalakouras (1993, Alexandroupoli), Greek international Volleyball player
- Stavros Stathakis (1987, Alexandroupoli), Greek football player
- Nikos Alavantas (1959, Orestiada), former Greek national football player
- Stefania Liberakaki (2002), Greek-Dutch singer with origin from Sofiko, a village near Didymoteicho
References
- ^ "Publication of provisional results of the 2011 Population Census" (PDF). National Statistical Service of Greece. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-07-03.
- ^ a b "Kallikratis reform law text" (PDF).
- ^ Law, Gwillim (1999). Administrative subdivisions of countries: a comprehensive world reference, 1900 through 1998. McFarland. p. 152. ISBN 978-0-7864-0729-3.
- ^ "Malamatina".