Ethyl heptanoate 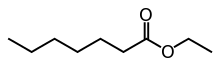 |
| Names |
| Preferred IUPAC name |
| Other names Heptanoic acid ethyl ester
Ethyl enanthate
Ethyl heptylate
Enanthic acid ethyl ester |
| Identifiers |
| | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.076  |
| | |
| UNII | |
| | |
InChI=1S/C9H18O2/c1-3-5-6-7-8-9(10)11-4-2/h3-8H2,1-2H3  Key: TVQGDYNRXLTQAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N  InChI=1/C9H18O2/c1-3-5-6-7-8-9(10)11-4-2/h3-8H2,1-2H3 Key: TVQGDYNRXLTQAP-UHFFFAOYAW
|
| |
| Properties |
Chemical formula | C9H18O2 |
| Molar mass | 158.241 g·mol−1 |
| Odor | Grape |
| Density | 0.860 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −66 °C (−87 °F; 207 K) |
| Boiling point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F; 461 to 462 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
| | |
Ethyl heptanoate is the ester resulting from the condensation of heptanoic acid and ethanol. It is used in the flavor industry because of its odor that is similar to grape.[1]
References
This article is copied from an
article on Wikipedia® - the free encyclopedia created and edited by its online user community. The text was not checked or edited by anyone on our staff. Although the vast majority of Wikipedia® encyclopedia articles provide accurate and timely information, please do not assume the accuracy of any particular article. This article is distributed under the terms of
GNU Free Documentation License.
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.
