 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 6,8-Didehydroestrone; Estra-1,3,5(10),6,8-pentaen-3-ol-17-one |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Estrogen |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.483 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H18O2 |
| Molar mass | 266.340 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
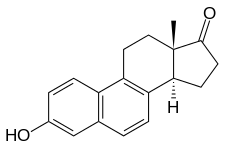
Equilenin, also known as 6,8-didehydroestrone, as well as estra-1,3,5(10),6,8-pentaen-3-ol-17-one, is a naturally occurring steroidal estrogen obtained from the urine of pregnant mares.[1][2] It is used as one of the components in conjugated estrogens (brand name Premarin).[2] It was the first complex natural product to be fully synthesized, in work reported by 1940 by Bachmann and Wilds.[3]
Chemistry
Synthesis
Total synthesis
The synthesis developed by the Bachmann group started from Butenand's ketone[4] – the 7-methoxy structural analog of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthren-1-one[5] – and which can be readily prepared from 1,6-Cleve's acid.[6] The approach was based on well-established transformations like the Claisen condensation, the Reformatsky reaction, the Arndt–Eistert reaction, and the Dieckmann condensation.[3] Nicolaou described this preparation as ending the era preceding the post-World War II work of Robert Burns Woodward that introduced enantioselective synthesis;[4] in this synthesis, a mixture of stereoisomers were prepared and then resolved,[6] and the choice of target was partly because of the existence of only two chiral carbons and hence only four stereoisomers.[5]
The overall yield of the synthesis was 2.7% based on a twenty-step process starting from Cleve's acid.[6]
See also
- List of estrogens § Equine estrogens
References
- ^ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 494–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b Fritz MA, Speroff L (28 March 2012). Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 751–. ISBN 978-1-4511-4847-3.
- ^ a b Bachmann WE, Cole W, Wilds AL (1940). "The Total Synthesis of the Sex Hormone Equilenin and Its Stereoisomers". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 (4): 824–839. doi:10.1021/ja01861a036.
- ^ a b Nicolaou KC, Vourloumis D, Winssinger N, Baran PS (January 2000). "The Art and Science of Total Synthesis at the Dawn of the Twenty-First Century" (PDF). Angewandte Chemie. 39 (1): 44–122. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000103)39:1<44::AID-ANIE44>3.0.CO;2-L. PMID 10649349. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-05-17. Retrieved 2017-07-22.
- ^ a b Bachmann WE, Cole W, Wilds AL (1939). "The Total Synthesis of the Sex Hormone Equilenin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 61 (4): 974–975. doi:10.1021/ja01873a513.
- ^ a b c Nakanishi K (1974). "Steroids". In Nakanishi K, Goto T, Itô S, Natori S, Nozoe S (eds.). Natural Products Chemistry. 1. Academic Press. pp. 421–545. ISBN 9781483218861.
