In combustion, a diffusion flame is a flame in which the oxidizer and fuel are separated before burning. Contrary to its name, a diffusion flame involves both diffusion and convection processes. The name diffusion flame was first suggested by S.P. Burke and T.E.W. Schumann in 1928,[1] to differentiate from premixed flame where fuel and oxidizer are premixed prior to burning. The diffusion flame is also referred to as nonpremixed flame. The burning rate is however still limited by the rate of diffusion.[2] Diffusion flames tend to burn slower and to produce more soot than premixed flames because there may not be sufficient oxidizer for the reaction to go to completion, although there are some exceptions to the rule. The soot typically produced in a diffusion flame becomes incandescent from the heat of the flame and lends the flame its readily identifiable orange-yellow color. Diffusion flames tend to have a less-localized flame front than premixed flames.
The contexts for diffusion may vary somewhat. For instance, a candle uses the heat of the flame itself to vaporize its wax fuel and the oxidizer (oxygen) diffuses into the flame from the surrounding air, while a gaslight flame (or the safety flame of a bunsen burner) uses fuel already in the form of a vapor.
Diffusion flames are often studied in counter flow (also called opposed jet) burners.[3] Their interest is due to possible application in the flamelet model for turbulent combustion. Furthermore they provide a convenient way to examine strained flames and flames with holes. These are also known under the name of "edge flames", characterized by a local extinction on their axis because of the high strain rates in the vicinity of the stagnation point.
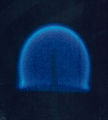
Diffusion flames have an entirely different appearance in a microgravity environment. There is no convection to carry the hot combustion products away from the fuel source, which results in a spherical flame front, such as in the candle seen here. This is a rare example of a diffusion flame which does not produce much soot and does not therefore have a typical yellow flame.
The common flame of a candle is a classic example of a diffusion flame. The yellow color of the flame is due to the large number of incandescent soot particles in the incomplete combustion reaction of the flame.
A nearly-turbulent diffusion flame
A candle in a microgravity environment. This is a rare example of a diffusion flame which does not produce much soot and does not therefore have a typical yellow flame
See also
- Burke–Schumann flame
- Liñán's diffusion flame theory
- Emmons problem
- Premixed flame
- Oxidizing and reducing flames
- Oxy-fuel combustion process
References
- ^ Burke, S. P., and T. E. W. Schumann. "Diffusion flames." Industrial & Engineering Chemistry 20.10 (1928): 998–1004.
- ^ https://inpressco.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Paper28183-197.pdf
- ^ Glassman, Irvin; Yetter, Richard A. (2008). "6. Diffusion Flames". Combustion. Burlington: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-088573-2.