 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
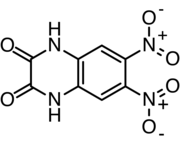
| IUPAC name 6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3(1H,4H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H4N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 252.142 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
DNQX (6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione) is a competitive antagonist at AMPA and kainate receptors, two ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) subfamilies.[1] It is used in a variety of molecular biology subfields, notably neurophysiology, to assist researchers in determining the properties of various types of ion channels and their potential applications in medicine.
See also
- Quinoxalinedione
- CNQX
References
- ^ Traynelis SF, Wollmuth LP, McBain CJ, Menniti FS, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Hansen KB, Yuan H, Myers SJ, Dingledine R (September 2010). "Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function". Pharmacological Reviews. 62 (3): 405–96. doi:10.1124/pr.109.002451. PMC 2964903. PMID 20716669.