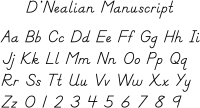D'Nealian, sometimes misspelled Denealian, is a style of writing and teaching cursive and manuscript ("print" and "block") handwriting for English. It derived from the Palmer Method and was designed to ease the learning of manuscript and cursive handwriting. D'Nealian was developed by Donald Thurber while teaching in a primary school, and was first introduced in 1978. The name of the script comes from Thurber's first name contracted with his middle name ("Neal").
The system was designed as a method to alleviate the problems with teaching children the traditional script method and the subsequent difficulty transitioning to cursive writing. D'Nealian manuscript form has many similarities to the cursive version. In theory, it is easier for children to learn and acquire basic handwriting skills using this method than traditional cursive writing.[1]
Description
The D'Nealian is a style of writing and teaching cursive handwriting for English, and is a derivative of the Palmer Method. It was designed to ease the learning of cursive and print handwriting.
History
D'Nealian was developed by Donald Thurber (December 15, 1927–January 6, 2020[2]), beginning in 1965, who did so while teaching in a primary school. The name of the script comes from Donald's first name contracted with his middle name ("Neal").
Criticism
D'Nealian has drawn criticism in many locations, as the addition of so-called "monkey tails"[3] to manuscript ("print-style" writing) effectively adds a "third step" to how children are instructed to write. Moreover, a common issue is that D'Nealian is taught extremely early, to first and second grade students, many of whom are still learning the rudiments of print-style writing. At times, some school districts have abruptly changed their teaching of handwriting, possibly causing difficulties for students who must then adapt to a different style.
A 1993 research review by Steve Graham concludes that "there is no credible evidence" that D'Nealian makes a difference in children's handwriting. He also states that D'Nealian creates practical problems for teachers (who must themselves learn the system and defend it to parents) and that it requires many young children to unlearn writing forms that they have already developed before formal instruction.[4]
See also
- Teaching script
References
- ^ Viadero, Debra (6 October 1993). "D'Nealian Handwriting Method Abandons 'Ball-and-Stick' Approach". Education Week. Retrieved 23 January 2018.
- ^ https://www.legacy.com/obituaries/toledoblade/obituary.aspx?n=donald-neal-thurber&pid=194992867
- ^ "Peterson Handwriting Q & A". mcnattlearningcenter.com. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ Sheehan, Robert J.; Graham, Steve (1993). "Are slanted manuscript alphabets superior to the traditional manuscript alphabet?". Childhood Education. 70 (2): 91–95. doi:10.1080/00094056.1993.10521001..