 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (5S,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-[(1R)-1-methylbutyl]-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H42 | |
| Molar mass | 330.59 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
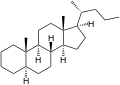
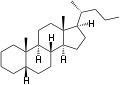
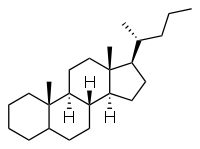
Cholane is a triterpene which can exist as either of two stereoisomers, 5α-cholane and 5β-cholane. Its name is derived from the Greek word for bile (χολή, chole) in reference to its original discovery from the bile of the American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana).[1] The compound itself has no known uses; however, various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals, typically in the form of sterols, steroids and bile acids (e.g. cholic acid).
See also
- Cholestane
- Ergostane
References
- ^ Kurauti, Yukiti; Kazuno, Taro (January 1939). "Tetraoxycholan, Trioxycholen und Trioxy-bis-norsterocholansäure aus der Galle von Rana Catesbina Shaw". Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift für physiologische Chemie (in German). 262 (1–2): 53–60. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1939.262.1-2.53.
External links
- Cholanes at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)