| "Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans" | |
|---|---|
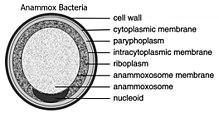 | |
| cell diagram of Brocadia anammoxidans | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Planctomycetes |
| Class: | Planctomycetia |
| Order: | Planctomycetales |
| Family: | Planctomycetaceae |
| Genus: | "Ca. Brocadia" |
| Species: | "Ca. B. anammoxidans" |
| Binomial name | |
| "Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans" | |
"Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans" is a bacterial member of the phylum Planctomycetes and therefore lacks peptidoglycan in its cell wall, and has a compartmentalized cytoplasm.
"Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans" was the first discovered organism capable of the anaerobic oxidation of ammonium, and it is the only organism known to produce hydrazine.[1] This process (dubbed the anammox-process) was discovered in the 1980s by the Gijs Kuenen lab in a waste water treatment plant in Delft, Netherlands. Ammonium oxidation is coupled to nitrite reduction to form the harmless dinitrogen gas.
The key enzyme involved in this reaction, hydroxylamine oxidoreductase, is located in an organelle-like structure called the anammoxosome. The ability to oxidize ammonium anaerobically makes "Candidatus Brocadia anammoxidans" potentially useful for reducing—or eliminating—ammonium from waste water.[2]
In waste treatment
Because of its ability to eliminate ammonium, a variety of uses have been found for this bacteria, particularly removal of nitrogen from waste streams.[3] The first full scale experiment employing the anammox process in the world was built at the waste water treatment plant Dokhaven/Sluisjesdijk in Rotterdam, Netherlands.[2]
Existing treatment plants use bacteria that convert ammonium into nitrate. The bacteria that do this need oxygen, which must be supplied by electric pumps. Denitrifying bacteria convert the nitrate into nitrogen gas. These require adding methanol. This process consumes an average of 44 watt-hours per day per person served by the sewage system.[2]
Researchers estimate that a methanogenic digester coupled to a nitrification-anammox bioreactor could generate 24 watt-hours per person per day, a net swing of 70 watt-hours.[2]
References
- ^ http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2005/11/1109_051109_rocketfuel.html
- ^ a b c d e Knight, Helen (7 May 2010). "Bugs will give us free power while cleaning our sewage". New Scientist. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ^ B. Kartal, G.J. Kuenen and M.C.M van Loosdrecht Sewage Treatment with Anammox, Science, 2010, vol 328 p 702-3