 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.744 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
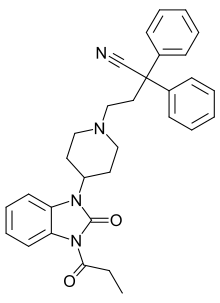
| Formula | C31H32N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 492.623 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bezitramide is an opioid analgesic. Bezitramide itself is a prodrug which is readily hydrolyzed in the gastrointestinal tract to its active metabolite, despropionyl-bezitramide.[1] Bezitramide was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1961.[2][3][4] It is most commonly marketed under the trade name Burgodin.
The drug was pulled from the shelves in the Netherlands in 2004 after fatal overdose cases, including one where a five-year-old child took one tablet from his mother's purse, ate it, and promptly died.[5]
Bezitramide is regulated much the same as morphine in all known jurisdictions and is a Schedule II substance under the United States' Controlled Substances Act of 1970, with an ACSCN of 9800 and zero annual manufacturing quota.[6] However, it has to this point never been marketed in the United States.
See also
- Benperidol
- Brorphine
- J-113,397
References
- ^ Meijer DK, Hovinga G, Versluis A, Bröring J, van Aken K, Moolenaar F, Wesseling H (1984). "Pharmacokinetics of the oral narcotic analgesic bezitramide and preliminary observations on its effect on experimentally induced pain". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 27 (5): 615–8. doi:10.1007/BF00556902. PMID 6519169. S2CID 23978449.
- ^ US patent 3196157, Janssen PA, "Benzimidalinyl Piperidines", published 1963-06-11, issued 1965-07-20
- ^ Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJ, Schellekens KH, Marsboom RH, Herin VV, Amery WK, et al. (June 1971). "Bezitramide (R 4845), a new potent and orally long-acting analgesic compound". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 21 (6): 862–7. PMID 5109278.
- ^ Knape H (April 1970). "Bezitramide, an orally active analgesic. An investigation on pain following operations for lumbar disc protrusion (preliminary report)". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 42 (4): 325–8. doi:10.1093/bja/42.4.325. PMID 4913411.
- ^ de Vos JC, Rohof OJ, Bernsen PJ, Conemans JM, van Unnik AJ (August 1983). "[Death caused by one tablet of Burgodin]". Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde. 127 (34): 1552–3. PMID 6633692.
- ^ Title 21 United States Code (USC) Controlled Substances Act