 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Kerlone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a609023 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral, ocular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 89% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 14–22 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (20%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.113.058 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
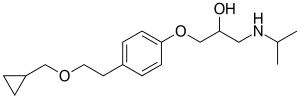
| Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 307.434 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Betaxolol is a selective beta1 receptor blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and glaucoma.[1] Being selective for beta1 receptors, it typically has fewer systemic side effects than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing bronchospasm (mediated by beta2 receptors) as timolol may. Betaxolol also shows greater affinity for beta1 receptors than metoprolol. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye (intraocular pressure). This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid (which is called the aqueous humor) within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to glaucoma.
It was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1983.[2]
Medical uses
- Oral: for the management of hypertension
- Ophthalmic: for the management of glaucoma
- the drug seems to have an effect of neuroprotection in glaucoma treatment
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the drug
- Patients with sinus bradycardia, heart block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, and overt cardiac failure
Side effects
History
Betaxolol was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for ocular use as a 0.5% solution (Betoptic) in 1985 and as a 0.25% solution (Betoptic S) in 1989.
Brand names
Brand names include Betoptic, Betoptic S, Lokren, Kerlone.
See also
- Levobetaxolol
- Cicloprolol
References
- ^ Buckley MM, Goa KL, Clissold SP (July 1990). "Ocular betaxolol. A review of its pharmacological properties, and therapeutic efficacy in glaucoma and ocular hypertension". Drugs. 40 (1): 75–90. doi:10.2165/00003495-199040010-00005. PMID 2202584. S2CID 46962082.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 461. ISBN 9783527607495.