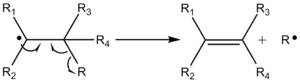
Beta scission is an important reaction in the chemistry of thermal cracking of hydrocarbons and the formation of free radicals. Free radicals are formed upon splitting the carbon-carbon bond. Free radicals are extremely reactive and short-lived. When a free radical in a polymer chain undergoes a beta scission, the free radical breaks two carbons away from the charged carbon producing an olefin (ethylene) and a primary free radical, which has two fewer carbon atoms.
In organic synthesis, beta scission can be used to direct multistep radical transformations. For example, beta-scission of a weak C-S bond was used to favor one of two equilibrating radicals in metal free conversion of phenols to aromatic esters and acids via C-O transposition.[1]
References
- ^ Baroudi, A.; Alicea, J.; Flack, P.; Kirincich,J.; Alabugin, I. V. Radical O→C Transposition: a Metal-Free Process forConversion of Phenols into Benzoates and Benzamides, J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 1521-37. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo102467j .(Highlighted in https://www.organic-chemistry.org/Highlights/2011/17October.shtm).