 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
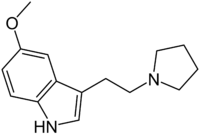
| IUPAC name 5-Methoxy-3-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)-1H-indole | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20N2O | |
| Molar mass | 244.338 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Off-white oil |
| Density | 200.3g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 164 to 167 °C (327 to 333 °F; 437 to 440 K) Melting point given for hydrochloride salt. |
| Boiling point | 160 to 170 °C (320 to 338 °F; 433 to 443 K) Boiling point for freebase at 0.05mm/Hg. |
| log P | 2.75270 |
| Vapor pressure | 7.42x10−07mm/Hg |
Refractive index (nD) | 1.614 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral, Vaporized | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Unknown, likely under several hours. | |
Duration of action | Several hours. |
| Legal status |
|
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 200.3 °C (392.5 °F; 473.4 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LDLo (lowest published) | 6250 μg/kg (Rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
5-MeO-pyr-T (5-methoxy-N,N-tetramethylenetryptamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the 5-methoxy analog of pyr-T. 5-MeO-pyr-T was first synthesized by Hunt & Brimblecombe,[1] who credited S. Mitzal for characterization of chemical properties.[2] Later human tests were reported by Alexander Shulgin, in his book TiHKAL. An oral dosage of 0.5 to 2 mg, and an inhaled dosage of 2–3 mg are reported. 5-MeO-pyr-T causes varying reactions, such as amnesia, tinnitus, vomiting, and a 5-MeO-DMT-like rushing sensation. At the highest dosage reported in TiHKAL, the subject describes awakening from an apparent fugue state during which they were wandering the streets, with complete amnesia upon awakening.[3]
Pharmacology
Testing was performed on rats using this compound while characterizing various agonists of the 5-HT7 receptor. It is an agonist with a Ki value of 630.96nM.[4]
Very little other data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 5-MeO-pyr-T.
See also
References
- ^ Hunt, R. R.; Brimblecombe, R. W. (July 1967). "Synthesis and Biological Activity of Some Ring-Substituted Tryptamines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (4): 646–648. doi:10.1021/jm00316a027.
- ^ Mitzal, S. (1962). "N/A". Dissertationes Pharm. 14: 305.
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Shulgin, Ann (1997). TiHKAL, The Continuation (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA, USA: Transform Press. pp. 548–551. ISBN 0-9630096-9-9. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ^ "AID 6666 - Binding affinity at rat 5-hydroxytryptamine 7 receptor. - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.