 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 234.299 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
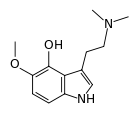
4-Hydroxy-5-methoxydimethyltryptamine, also known as 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT or psilomethoxin, is a novel psychedelic drug. It is the 4-hydroxy counterpart of 5-MeO-DMT, or the 5-methoxy counterpart of psilocin.
It is a psychedelic tryptamine but very little is known about it. The only report of it in the chemical literature was a paper published by Marc Julia's group at the Pasteur Institute in 1965.[1] This paper reports a 10 step synthesis of 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT from ortho-vanillin. However, Alexander Shulgin has explained that it could be possible to cultivate 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT in psilocybin mushrooms by adding 5-MeO-DMT to the growing substrate of the fungus. Though this method has never been explored with 5-MeO-DMT, it has been used successfully for changing DET into 4-HO-DET and 4-PO-DET, both of which had never before been found in nature.[2]
Manufacture, transportation, possession, and distribution of 4-HO-5-MeO-DMT in the United States may be illegal under the Federal Analogue Act due to its structural relation to psilocin, which is listed as a Schedule I narcotic under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970.
Due to the resemblance to the neurotoxin 4,5-dihydroxytryptamine,[3] there is some concern that this compound may share that neurotoxicity, though this has not been investigated.
References
- ^ Julia M, Manoury P, Voillaume MC (1965). "[No 209 - Recherches en série indolique. XIV (*) - Sur des méthoxy-5 hydroxy-4, méthoxy-5 hydroxy-6 et méthoxy-7 hydroxy-6 tryptamines]". Bull Chim Soc Fr (in French): 1417–23.
- ^ Gartz J (1989). "Biotransformation of tryptamine derivatives in mycelial cultures of Psilocybe". Journal of Basic Microbiology. 29 (6): 347–52. doi:10.1002/jobm.3620290608. PMID 2614674.
- ^ Björklund A, Nobin A, Stenevi U (December 1973). "The use of neurotoxic dihydroxytryptamines as tools for morphological studies and localized lesioning of central indolamine neurons". Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie. 145 (4): 479–501. doi:10.1007/BF00306720. PMID 4774982. S2CID 44044588.