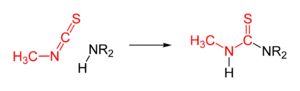| | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Methylisothiocyanate | |||
| Other names MITC | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.303 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
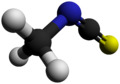
Chemical formula | C2H3NS | ||
| Molar mass | 73.12 | ||
| Appearance | colourless solid | ||
| Density | 1.07 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 31 °C (88 °F; 304 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 117 °C (243 °F; 390 K) | ||
| 8.2g/L | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | ACC# 07204 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Structure | |||
Dipole moment | 3.528 D | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds | Methyl isocyanate Methyl thiocyanate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Methyl isothiocyanate is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3N=C=S. This low melting colorless solid is a powerful lachrymator. As a precursor to a variety of valuable bioactive compounds, it is the most important organic isothiocyanate in industry.[1]
Synthesis
It is prepared industrially by two routes. Annual production in 1993 was estimated to be 4M kg. The main method involves the thermal rearrangement of methyl thiocyanate:[1]
- CH3S-C≡N → CH3N=C=S
It is also prepared via with the reaction of methylamine with carbon disulfide followed by oxidation of the resulting dithiocarbamate with hydrogen peroxide. A related method is useful to prepare this compound in the laboratory.[2]
MITC forms naturally upon the enzymatic degradation of glucocapparin, a modified sugar found in capers.
Reactions
A characteristic reaction is with amines to give methyl thioureas:
- CH3NCS + R2NH → R2NC(S)NHCH3
Other nucleophiles add similarly.
Applications
Solutions of MITC are used in agriculture as soil fumigants, mainly for protection against fungi and nematodes.
MITC is a building block for the synthesis of 1,3,4-thiadiazoles, which are heterocyclic compounds used as herbicides. Commercial products include "Spike", "Ustilan," and "Erbotan."
Well known pharmaceuticals prepared using MITC include Zantac and Tagamet. Suritozole is a third example.
MITC is used in the Etasuline patent (Ex2[3]), although the compound is question (Ex6) is with EITC.
Safety
MITC is a dangerous lachrymator as well as being poisonous.
See also
- 6-MITC
References
- ^ a b Romanowski, F.; Klenk, H. "Thiocyanates and Isothiocyanates, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_749.
- ^ Moore, M. L.; Crossley, F. S. (1941). "Methyl Isothiocyanate". Organic Syntheses. 21: 81.; Collective Volume, 3, p. 599
- ^ U.S. Patent 3,417,085