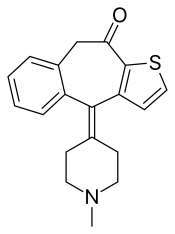
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zaditor[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604033 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets), topical eye drops |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60% |
| Protein binding | 75% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.348 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19NOS |
| Molar mass | 309.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ketotifen, sold under the brand name Zaditor among others, is a second-generation noncompetitive H1-antihistamine and mast cell stabilizer. It is most commonly sold as a salt with fumaric acid, ketotifen fumarate, and is available in two forms. In its ophthalmic form, it is used to treat allergic conjunctivitis.[1] In its oral form, it is used to prevent asthma attacks or anaphylaxis, as well as various mast cell, allergic-type disorders.[2][3][4][5][6]
It was patented in 1970 and came into medical use in 1976.[7]
Medical uses
Ketotifen relieves and prevents eye itchiness and/or irritation associated with most seasonal allergies. It starts working within minutes after administering the drops. The drug has not been studied in children under three.[1] The mean elimination half life is 12 hours.[8] Besides its anti-histaminic activity, it is also a functional leukotriene antagonist and a phosphodiesterase inhibitor.
"[O]ral ketotifen has been used in patients with asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis, chronic urticaria, cold-induced urticaria, cholinergic urticaria, exercise-induced urticaria, [systemic mast cell disease including mastocytosis, MCAS, allergic and nonallergic anaphylaxis, angioedema], and food allergy in Canada, Europe, and Mexico." Now available via prescription at US compounding pharmacies: "For adults and older children with asthma or allergic disease, the recommended dose of ketotifen is 1 mg twice daily." "FDA staff did recommend more extensive evaluations for management of urticaria."[4][5]
The drug may also help relieve irritable bowel syndrome.[9]
Side effects
Side effects include drowsiness, weight gain (11-12lbs), dry mouth, irritability, and increased nosebleeds.[10]
Pharmacology
Ketotifen is a selective antihistamine – that is, an inverse agonist of the histamine H1 receptor (Ki = 0.166 nM)[11] – and mast cell stabilizer.[12] In addition, ketotifen has weak anticholinergic (Ki = 204 nM for mACh) and antiserotonergic (Ki = 38.9 nM for 5-HT2A) activity.[11][13] However, at the dosages in which it is typically used clinically, both the anticholinergic and antiserotonergic activity of ketotifen are said not to be appreciable.[14]
Society and culture
Brand names
Ketotifen is marketed under many brand names worldwide.[15]
References
- ^ a b c "Zaditor- ketotifen fumarate solution". DailyMed. 13 February 2020. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- ^ Sokol, Kristin C.; Amar, Neil K.; Starkey, Jonathan; Grant, J. Andrew (2013). "Ketotifen in the management of chronic urticaria: Resurrection of an old drug". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 111 (6): 433–6. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2013.10.003. PMC 4309375. PMID 24267353.
- ^ Shawky, Rabah M.; Seifeldin, Neveen S. (2015). "The relation between antihistamine medication during early pregnancy & birth defects". Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics. 16 (4): 287–90. doi:10.1016/j.ejmhg.2015.04.003.
- ^ a b Zuberbier, Torsten (2012). "A Summary of the New International EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/ WAO Guidelines in Urticaria". World Allergy Organization Journal. 5 (1): S1–S5. doi:10.1186/1939-4551-5-S1-S1. PMC 3488932. PMID 23268477.
- ^ a b Zuberbier, T.; Asero, R.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Walter Canonica, G.; Church, M. K.; Giménez-Arnau, A. M.; Grattan, C. E. H.; Kapp, A.; Maurer, M.; Merk, H. F.; Rogala, B.; Saini, S.; Sánchez-Borges, M.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Schünemann, H.; Staubach, P.; Vena, G. A.; Wedi, B. (2009). "EAACI/GA²LEN/EDF/WAO guideline: Management of urticaria". Allergy. 64 (10): 1427–43. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02178.x. PMID 19772513. S2CID 14587946.
- ^ Li, Zhenhong; Celestin, Jocelyn (February 23, 2015). Ketotifen: A Role in the Treatment of Idiopathic Anaphylaxis. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Annual Meeting. Houston.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 548. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Grahnén, A.; Lönnebo, A.; Beck, O.; Eckernäs, S-Å; Dahlström, B.; Lindström, B. (1992). "Pharmacokinetics of ketotiffn after oral administration to healthy male subjects". Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition. 13 (4): 255–62. doi:10.1002/bdd.2510130404. PMID 1600111. S2CID 72293850.
- ^ Klooker, T. K.; Braak, B.; Koopman, K. E.; Welting, O.; Wouters, M. M.; Van Der Heide, S.; Schemann, M.; Bischoff, S. C.; Van Den Wijngaard, R. M.; Boeckxstaens, G. E. (2010). "The mast cell stabiliser ketotifen decreases visceral hypersensitivity and improves intestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome" (PDF). Gut. 59 (9): 1213–21. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.213108. PMID 20650926. S2CID 18889707.
- ^ "Zaditen - MIMS online". www.mims.co.uk.
- ^ a b Kakiuchi M, Ohashi T, Musoh K, Kawamura K, Morikawa K, Kato H (1997). "Studies on the novel antiallergic agent HSR-609: its penetration into the central nervous system in mice and guinea pigs and its selectivity for the histamine H1-receptor". Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 73 (4): 291–8. doi:10.1254/jjp.73.291. PMID 9165365.
- ^ Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams (2008). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1019–. ISBN 978-0-7817-6879-5.
- ^ V Alagarsamy (16 June 2012). Textbook of Medicinal Chemistry Vol II - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 38–. ISBN 978-81-312-3259-0.
- ^ Jürgen Drews (6 December 2012). Immunopharmacology: Principles and Perspectives. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 282–. ISBN 978-3-642-75561-3.
- ^ "Ketotifen International". Drugs.com. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
External links
- "Ketotifen". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.