A tricarboxylic acid is an organic carboxylic acid whose chemical structure contains three carboxyl functional groups (-COOH). The best-known example of a tricarboxylic acid is citric acid.
Uses
Citric acid cycle
Citric acid, a type of tricarboxylic acid, is used in the citric acid cycle – also known as tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or Krebs cycle – which is fundamental to all aerobic organisms.
Examples
| Common name | IUPAC name | Molecular formula | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid | 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 | |
| Isocitric acid | 1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 | |
| Aconitic acid | Prop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H6O6 | (cis-form & trans-form) |
| Propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | Propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C3H5(COOH)3 | |
| Agaric acid | 2-Hydroxynonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C22H40O7 | 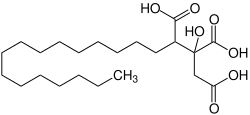 |
| Trimesic acid | benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid | C9H6O6 |
See also
- Citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)
- Dicarboxylic acid
- Mellitic acid
Literature
- Ryan J. Mailloux, Robin Bériault, Joseph Lemire, Ranji Singh, Daniel R. Chénier, Robert D. Hamel, Vasu D. Appanna (2007). "The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle, an Ancient Metabolic Network with a Novel Twist". PLOS ONE. Retrieved 2016-07-21.