 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
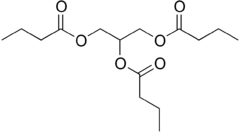
| IUPAC name 1,3-Di(butanoyloxy)propan-2-yl butanoate | |
| Other names Tributyrin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.410 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C15H26O6 |
| Molar mass | 302.367 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Oily liquid with bitter taste[1] |
| Density | 1.032 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −75 °C (−103 °F; 198 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 305 to 310 °C (581 to 590 °F; 578 to 583 K)[1] |
| Insoluble[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Tributyrin MSDS, Fischer Scientific |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Tributyrin is a triglyceride naturally present in butter. It is an ester composed of butyric acid and glycerol.[1] Among other things, it is used as an ingredient in making margarine. It is present in butter and can be described as a liquid fat with an acrid taste.
Tributyrin is also used in microbiological laboratories to identify the bacterium Moraxella catarrhalis. [2]
Tributyrin is a stable and rapidly absorbed prodrug of butyric acid which enhances antiproliferative effects of dihydroxycholecalciferol in human colon cancer cells.[3]
References
- ^ a b c d e f Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996), The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.), Merck, ISBN 0911910123
- ^ Pérez, José L.; Angeles Pulido; Florencia Pantozzi; Rogelio Martin (October 1990). "Butyrate esterase (4-methylumbelliferyl butyrate) spot test, a simple method for immediate identification of Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis corrected" (PDF Reprint). Journal of Clinical Microbiology. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology. 28 (10): 2347–2348. ISSN 1098-660X. PMC 268174. PMID 2121784.
- ^ Gaschott, Tanja; Dieter Steinhilber; Vladan Milovic; Jürgen Stein (June 2001). "Tributyrin, a Stable and Rapidly Absorbed Prodrug of Butyric Acid, Enhances Antiproliferative Effects of Dihydroxycholecalciferol in Human Colon Cancer Cells". The Journal of Nutrition. Bethesda, MD: The American Society for Nutritional Sciences. 131 (6): 1839–1843. doi:10.1093/jn/131.6.1839. ISSN 1541-6100. PMID 11385076. Retrieved 2009-08-17.