TOM, or methylthio-methyl-methoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs and substituted amphetamines with the molecular formula C12H19NOS. 2-TOM and 5-TOM are the 2- and 5-methylthio analogs of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM), respectively. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his book PiHKAL.[1][2] Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
2-TOM
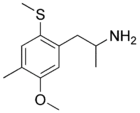
2-TOM, or 5-methoxy-4-methyl-2-methylthio-amphetamine
- Dosage: 60–100 mg
- Duration: 8–10 hours
- Effects: strong closed-eye visuals upon listening to music
5-TOM
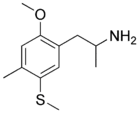
5-TOM, or 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-methylthio-amphetamine
- Dosage: 30–50 mg
- Duration: 6–10 hours
- Effects: open and closed-eye visuals, psychedelia, hallucinations
See also
References
This article is copied from an
article on Wikipedia® - the free encyclopedia created and edited by its online user community. The text was not checked or edited by anyone on our staff. Although the vast majority of Wikipedia® encyclopedia articles provide accurate and timely information, please do not assume the accuracy of any particular article. This article is distributed under the terms of
GNU Free Documentation License.
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.

