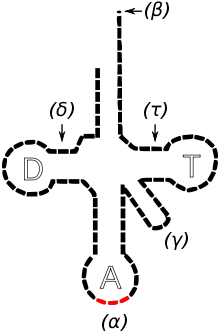
The T-arm or T-loop is a specialized region on the tRNA molecule which acts as a special recognition site for the ribosome to form a tRNA-ribosome complex during protein biosynthesis or translation (biology).
The T-arm has two components to it; the T-stems and the T-loop.
- There are two T-stems of five base pairs each. T-stem 1 is from 49-53 and T-stem 2 is from 61-65.
- The T-loop is also often known as the TΨC arm due to the presence of thymidine, pseudouridine and cytidine residues.
Organisms with T-loop lacking tRNA exhibit a much lower level of aminoacylation and EF-Tu-binding than in organisms which have the native tRNA.
This article is copied from an
article on Wikipedia® - the free encyclopedia created and edited by its online user community. The text was not checked or edited by anyone on our staff. Although the vast majority of Wikipedia® encyclopedia articles provide accurate and timely information, please do not assume the accuracy of any particular article. This article is distributed under the terms of
GNU Free Documentation License.
All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. This information should not be considered complete, up to date, and is not intended to be used in place of a visit, consultation, or advice of a legal, medical, or any other professional.