| Sensory decussation | |
|---|---|
 The sensory tract | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | decussatio lemnisci medialis |
| NeuroNames | 788 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
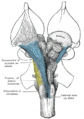
The sensory decussation or decussation of the lemnisci is a decussation or crossover of axons from the gracile nucleus and cuneate nucleus, which are responsible for fine touch, vibration, proprioception and two-point discrimination of the body. The fibres of this decussation are called the internal arcuate fibres and are found at the superior aspect of the closed medulla superior to the motor decussation. It is part of the second neuron in the posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway.
Structure
At the level of the closed medulla in the posterior white column, two large nuclei namely the gracile nucleus and the cuneate nucleus can be found. The two nuclei receive the impulse from the two ascending tracts: fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus. After the two tracts terminate upon these nuclei, the heavily myelinated fibres arise and ascend anteromedially around the periaqueductal gray as internal arcuate fibres. These fibres decussate (cross) to the contralateral (opposite) side, so called the sensory decussation. The ascending bundle after the decussation is called the medial lemniscus. Unlike other ascending tracts of the brain, fibres of the medial lemniscus do not give off collateral branches as they travel along the brainstem.[1]
Function
The fibres that make up the sensory decussation are responsible for fine touch, proprioception and two-point discrimination of the whole body excluding the head.[1]
Additional images
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 777 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Core Text of Neuroanatomy (4 Sub ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. 1991-08-01. ISBN 9780683014570.
External links
- Image at umd.edu