 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.772 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
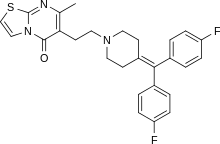
| Formula | C27H25F2N3OS |
| Molar mass | 477.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ritanserin (INN, USAN, BAN) is a serotonin receptor antagonist which was never marketed for clinical use but has been used in scientific research.[1]
Research
Ritanserin was tested in clinical trials for schizophrenia[2] and migraine.[3]
Pharmacology
Ritanserin acts as a selective 5-HT2A (Ki = 0.45 nM) and 5-HT2C receptor (Ki = 0.71 nM) antagonist.[2][4] It has relatively low affinity for the H1, D2, α1-adrenergic, and α2-adrenergic receptors (39-, 77-, 107-, and 166-fold lower relative to 5-HT2A, respectively).[4] The affinity of ritanserin for the 5-HT1A receptor is less than 1 μM.[4] In addition to its affinity for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, ritanserin also binds to and antagonizes the 5-HT1D, 5-HT2B, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors.[5]
The atypical antipsychotic risperidone was developed from ritanserin.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Dr. Ian Morton; I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (31 October 1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 249–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9.
- ^ a b Akhondzadeh S, Malek-Hosseini M, Ghoreishi A, Raznahan M, Rezazadeh SA (September 2008). "Effect of ritanserin, a 5HT2A/2C antagonist, on negative symptoms of schizophrenia: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study". Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. 32 (8): 1879–83. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.08.020. PMID 18801405. S2CID 12270281.
- ^ Nappi, G; Sandrini, G; Granella, F; Ruiz, L; Cerutti, G; Facchinetti, F; Blandini, F; Manzoni, GC (June 1990). "A new 5-HT2 antagonist (ritanserin) in the treatment of chronic headache with depression. A double-blind study vs amitriptyline". Headache. 30 (7): 439–44. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.1990.hed3007439.x. hdl:11380/740716. PMID 2119355. S2CID 25781431.
- ^ a b c Leysen JE, Gommeren W, Van Gompel P, Wynants J, Janssen PF, Laduron PM (1985). "Receptor-binding properties in vitro and in vivo of ritanserin: A very potent and long acting serotonin-S2 antagonist". Mol Pharmacol. 27 (6): 600–11. PMID 2860558.
- ^ Harmful Non-Indigenous Species in the United States. DIANE Publishing. 1 February 1993. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-0-7881-0441-1.
- ^ Bentham Science Publishers (May 1994). Current Medicinal Chemistry. Bentham Science Publishers. pp. 52–.