South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region | |
|---|---|
Autonomous region | |
| Anthem: "Autonomy" | |
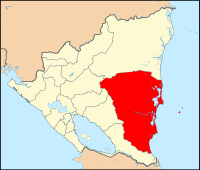 Location of the South Caribbean Autonomous Region in Nicaragua. | |
| Coordinates: 12°0′N 83°45′W / 12.000°N 83.750°W | |
| Country | |
| Largest city | Bluefields |
| Capital | Bluefields |
| Municipalities | List
|
| Government | |
| • Type | Autonomous |
| • Body | Autonomous Regional Council of the South Caribbean Coast |
| • Regional Coordinator (Governor) | Rubén López Espinoza (FSLN) |
| Area rank | 2nd (20.9% of Nicaragua) |
| Population (2019 estimate)[1] | |
| • Total | 408,326 |
| • Rank | 7th (6.0% of Nicaragua) |
| ISO 3166 code | NI-AS |
| Autonomy Statute | 30 October 1987 |
| Official languages | Regional Creole (Miskito Coast Creole and Rama Cay Creole) Miskito Sumo (Mayangna and Ulwa) Garifuna Rama English |
| Regional Council | 47 councilors |
| National Assembly | 2 deputies (of 92) |
The South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region is one of two autonomous regions in Nicaragua. It covers an area of 27,260 km2 (10,530 sq mi) and has a population of 408,326 (2019 estimate). The capital is Bluefields. Bordering the Caribbean Sea, it contains part of the region known as the Mosquito Coast.
The Pearl Cays archipelago of islands is also a part of the South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region.
See also
- North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region
External links
- The autonomous regions of Nicaragua's Caribbean Coast
- From Conflict to Autonomy in Nicaragua: Lessons Learnt, report by Minority Rights Group International, April 2007
References
- ^ Citypopulation.de Population of departments in Nicaragua