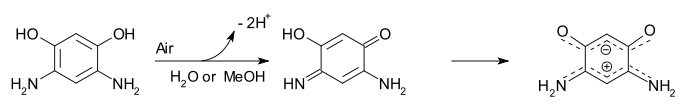
A quinonoid zwitterion is a special type of zwitterion (or more precisely Mesoionic) based on quinone related chemical compounds. The benzene derivate 1,3-dihydroxy-4,6-diaminobenzene is easily oxidized by air in water or methanol to the quinonoid. This compound was first prepared in 1883 and the quinonoid structure first proposed in 1956. In 2002 the compound was found to be more stable and to exist as the zwitterion after a proton transfer. Evidence for this structure is based on NMR spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography. The positive charge is delocalized between the amino groups over 4 bonds involving 6 pi electrons. The negative charge is spread likewise between the oxygen atoms.
See also
References
- Qing-Zheng Yang, Olivier Siri and Pierre Braunstein Chemical Communications, 2005, (21), 2660 - 2662 Abstract
- Olivier Siri and Pierre Braunstein Chemical Communications, 2002, (3), 208 - 209 Abstract