Oxazines are heterocyclic compounds containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom in a doubly unsaturated six-membered ring. Isomers exist depending on the relative position of the heteroatoms and relative position of the double bonds.
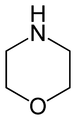
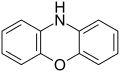
By extension, the derivatives are also referred to as oxazines; examples include ifosfamide and morpholine (tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine). A commercially available dihydro-1,3-oxazine is a reagent in the Meyers synthesis of aldehydes. Fluorescent dyes such as Nile red and Nile blue are based on the aromatic benzophenoxazine. Cinnabarine and cinnabaric acid are two naturally occurring dioxazines, being derived from biodegradation of tryptophan.[2]
Dioxazines
Dioxazines are pentacyclic compounds consisting of two oxazine subunits. A commercially important example is the pigment pigment violet 23.[3]

Benzoxazines
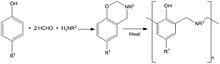
Benzoxazines formed by the reaction of phenols, formaldehyde and primary amines which on heating to ~200 °C (~400 °F) polymerise to produce polybenzoxazine networks.[5] The resulting high molecular weight thermoset polymer matrix composites are used where enhanced mechanical performance, flame and fire resistance compared to epoxy and phenolic resins is required.[6]
Images
References
- ^ Theophil Eicher, Siegfried Hauptmann, Andreas Speicher: The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Structures, Reactions, Synthesis, and Applications, 3rd, Completely Revised and Enlarged Edition, John Wiley & Sons, p. 442 (Oxazines, p. 442, at Google Books).
- ^ Stone, Trevor W.; Stoy, Nicholas; Darlington, L. Gail "An expanding range of targets for kynurenine metabolites of tryptophan" Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2013, volume 34, pp. 136-143.
- ^ Chamberlain, Terence "Dioxazine violet pigments" from High Performance Pigments Edited by Smith, Hugh M. 2002,185-194. doi:10.1002/3527600493.ch12
- ^ Horst Tappe, Walter Helmling, Peter Mischke, Karl Rebsamen, Uwe Reiher, Werner Russ, Ludwig Schläfer and Petra Vermehren "Reactive Dyes"in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_651
- ^ "BENZOXAZINE CHEMISTRY: A NEW MATERIAL TO MEET FIRE RETARDANT CHALLENGES OFAEROSPACE INTERIORS APPLICATIONS" (PDF).
- ^ Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins, ed. Hatsuo Ishida And Tarek Agag, Elsevier B.V., 2011, ISBN 978-0-444-53790-4
External links
- Oxazines at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Development of polymeric materials as a class of benzoxazines