| Medial rectus | |
|---|---|
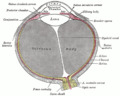
 Rectus muscles: 2 = superior, 3 = inferior, 4 = medial, 5 = lateral Oblique muscles: 6 = superior, 8 = inferior Other muscle: 9 = levator palpebrae superioris Other structures: 1 = Annulus of Zinn, 7 = Trochlea, 10 = Superior tarsus, 11 = Sclera, 12 = Optic nerve | |
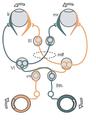
 Figure showing the mode of innervation of the Recti medialis and lateralis of the eye. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex |
| Insertion | 5.5 mm medial to the limbus |
| Nerve | inferior division of the oculomotor nerve |
| Actions | adducts the eyeball (makes it move inwards) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rectus medialis bulbi |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.012 |
| TA2 | 2044 |
| FMA | 49037 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
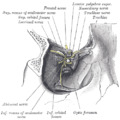
The medial rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit.
As with most of the muscles of the orbit, it is innervated by the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III).
This muscle shares an origin with several other extrinsic eye muscles, the anulus tendineus, or common tendon.
It is shorter but stronger than the other orbital recti muscles.[1]
Additional images
References
- ^ Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Limited. pp. 666–685. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 29:01-06 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit4)
- Diagram at howstuffworks.com