In optometry, the least distance of distinct vision (LDDV) or the reference seeing distance (RSD) is the closest someone with "normal" vision (20/20 vision) can comfortably look at something. In other words, LDDV is the minimum comfortable distance between the naked human eye and a visible object.
magnifying power (M) of a lens with focal length (f in millimeters) when viewed by the naked human eye:
See also
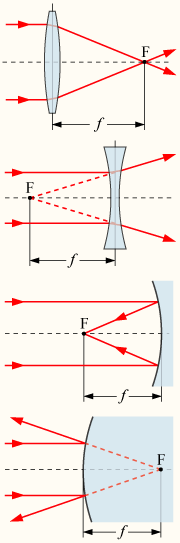
The power of a lens or curved mirror in Dioptres is calculated by the relationship D=1/F, where D is the power in Dioptres and F is the focal length of the device in metres. A convex lens and a concave mirror have positive focal lengths, and hence their strength in Dioptres is also positive. If the lens is concave or the mirror is convex, the focal length, and hence the power in Dioptres, is negative.