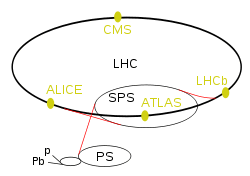
 | |
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| FASER | ForwArd Search ExpeRiment |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 4) and lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
The LHCf (Large Hadron Collider forward) is a special-purpose Large Hadron Collider experiment for astroparticle (cosmic ray) physics, and one of eight detectors in the LHC accelerator at CERN. The other seven are: ATLAS, ALICE, CMS, MoEDAL, TOTEM, LHCb and FASER. LHCf is designed to study the particles generated in the "forward" region of collisions, those almost directly in line with the colliding proton beams. It therefore consists of two detectors, 140 m on either side of the interaction point. Because of this large distance, it can co-exist with a more conventional detector surrounding the interaction point, and shares the interaction point IP1 with the much larger general-purpose ATLAS experiment.
Purpose
The LHCf is intended to measure the energy and numbers of neutral pions (
π0
) produced by the collider. This will hopefully help explain the origin of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. The results will complement other high-energy cosmic ray measurements from the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina, and the Telescope Array Project in Utah.
References
- LHCf section on US/LHC Website
- LHCf: a tiny new experiment joins the LHC, CERN Courier, Nov 1, 2006, retrieved on 2009-03-25. (Describes the location of the experiment.)
- The LHCf experiment at LHC
- Technical Design Report of LHCf
- O Adriani et al. (LHCf Collaboration) (2008). "The LHCf detector at the CERN Large Hadron Collider". Journal of Instrumentation. 3 (8): S08006. Bibcode:2008JInst...3S8006L. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/3/08/S08006. hdl:10550/42770. (Full design documentation)
- O Adriani et al. (LHCf Collaboration) (2013). "LHCf detector performance during the 2009-2010 LHC run". International Journal of Modern Physics A. 28 (25): 1330036–1. Bibcode:2013IJMPA..2830036A. doi:10.1142/S0217751X13300366. (Full design documentation)
External links
